Bible code: Difference between revisions
Damonthesis (talk | contribs) m (fixed tag/spelling) |
Damonthesis (talk | contribs) m |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
Though Bible codes have been postulated and studied for centuries, the subject has been popularized in modern times by Michael Drosnin's book ''[[The Bible Code (book)|The Bible Code]]'' and the movie ''[[The Omega Code]]''. |
Though Bible codes have been postulated and studied for centuries, the subject has been popularized in modern times by Michael Drosnin's book ''[[The Bible Code (book)|The Bible Code]]'' and the movie ''[[The Omega Code]]''. |
||
| − | Many examples have been documented in the past. One cited example is that by taking every 49th letter of the [[Book of Genesis]] starting with the first [[taw]], the Hebrew word "[[torah]]" is spelled out, the same happens in the [[Book of Exodus]]. The word "[[torah]]" is spelled in reverse order, in the same manner, in the [[Book of Numbers]] and the [[Book of Deuteronomy]]. The [[Book of Leviticus]], contains the [[ |
+ | Many examples have been documented in the past. One cited example is that by taking every 49th letter of the [[Book of Genesis]] starting with the first [[taw]], the Hebrew word "[[torah]]" is spelled out, the same happens in the [[Book of Exodus]]. The word "[[torah]]" is spelled in reverse order, in the same manner, in the [[Book of Numbers]] and the [[Book of Deuteronomy]]. The [[Book of Leviticus]], contains the [[Tetragramatton]] encoded using ELS with a skip of 7, with all four other books pointing towards it. The word Modern computers have been used to search for similar patterns and more complex variants, and published as a "challenging puzzle" in a peer-reviewed academic journal in 1994. Proponents hold that it is exceedingly unlikely such sequences could arise by chance, while skeptics and opponents hold that such sequences do often arise by chance, as demonstrated on other Hebrew and English texts.<ref>{{cite web | url="http://unitedisrael.org/blog/2009/11/" | title="Bible Codes: Looking Back a Dozen Years" }}</ref> |
==Overview== |
==Overview== |
||
Revision as of 20:18, 30 April 2013
The Bible code (Hebrew: צפנים בתנ"ך), also known as the Torah code, is a purported set of secret messages encoded within the Hebrew text of the Torah. This hidden code has been described as a method by which specific letters from the text can be selected to reveal an otherwise obscured message. Though Bible codes have been postulated and studied for centuries, the subject has been popularized in modern times by Michael Drosnin's book The Bible Code and the movie The Omega Code.
Many examples have been documented in the past. One cited example is that by taking every 49th letter of the Book of Genesis starting with the first taw, the Hebrew word "torah" is spelled out, the same happens in the Book of Exodus. The word "torah" is spelled in reverse order, in the same manner, in the Book of Numbers and the Book of Deuteronomy. The Book of Leviticus, contains the Tetragramatton encoded using ELS with a skip of 7, with all four other books pointing towards it. The word Modern computers have been used to search for similar patterns and more complex variants, and published as a "challenging puzzle" in a peer-reviewed academic journal in 1994. Proponents hold that it is exceedingly unlikely such sequences could arise by chance, while skeptics and opponents hold that such sequences do often arise by chance, as demonstrated on other Hebrew and English texts.[1]
Overview
Contemporary discussion and controversy around one specific encryption method became widespread in 1994 when Doron Witztum, Eliyahu Rips and Yoav Rosenberg published a paper, "Equidistant Letter Sequences in the Book of Genesis", in the scientific journal Statistical Science.[2] The paper, which was presented by the journal as a "challenging puzzle", presented strong statistical evidence that biographical information about famous rabbis was encoded in the text of the Book of Genesis, centuries before those rabbis lived.
Since then the term "Bible codes" has been popularly used to refer specifically to information encrypted via this ELS method.
Since the Witztum, Rips and Rosenberg (WRR) paper was published, two conflicting schools of thought regarding the "codes" have emerged among proponents. The traditional (WRR) view of the codes is based strictly on their applicability to the Torah, and asserts that any attempt to study the codes outside of this context is invalid. This is based on a belief that the Torah is unique among biblical texts in that it was given directly to mankind (via Moses) in exact letter-by-letter sequence and in the original Hebrew language.
Equidistant Letter Sequence method
The primary method by which purportedly meaningful messages have been extracted is the Equidistant Letter Sequence (ELS). To obtain an ELS from a text, choose a starting point (in principle, any letter) and a skip number, also freely and possibly negative. Then, beginning at the starting point, select letters from the text at equal spacing as given by the skip number. For example, the bold letters in this sentence form an ELS. With a skip of −4, and ignoring the spaces and punctuation, the word safest is spelled out.
Often more than one ELS related to some topic can be displayed simultaneously in an ELS letter array. This is produced by writing out the text in a regular grid, with exactly the same number of letters in each line, then cutting out a rectangle. In the example below, part of the King James Version of Genesis (26:5–10) is shown with 33 letters per line. ELSs for BIBLE and CODE are shown. Normally only a smaller rectangle would be displayed, such as the rectangle drawn in the figure. In that case there would be letters missing between adjacent lines in the picture, but it is essential that the number of missing letters be the same for each line.
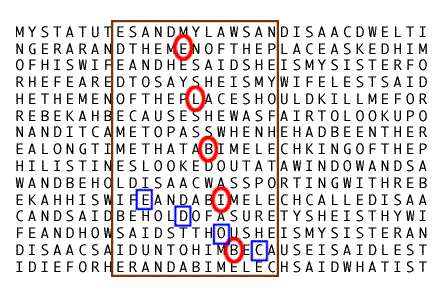
Although the above examples are in English texts, Bible codes proponents usually use a Hebrew Bible text. For religious reasons, most Jewish proponents use only the Torah (Genesis–Deuteronomy).
ELS extensions
Once a specific word has been found as an ELS, it is natural to see if that word is part of a longer ELS consisting of multiple words.[3] For example, in the middle of the rightmost column of the boxed matrix above is the ELS "he". After searching immediately above and below this ELS, we see another ELS ("toe") that is right below the "he" ELS. Code pioneers Haralick and Rips have published an example of a longer, extended ELS, which reads, "Destruction I will call you; cursed is Bin Laden and revenge is to the Messiah."[4]
ELS extensions that form phrases or sentences are of interest. It follows from the basics of probability theory that the longer the extended ELS, the less likely it is to be the result of chance.[5]
History
Jewish culture has a long tradition of interpretation, annotation, and commentary regarding the Bible, leading to both exegesis and eisegesis (insightful and false interpretations). The Bible code can be viewed as a part of this tradition, albeit one of the more controversial parts. Throughout history, many Jewish, and later Christian, scholars have attempted to find hidden or coded messages within the Bible's text, notably including Isaac Newton.[6][7]
The 13th-century Spanish Rabbi Bachya ben Asher may have been the first[citation needed] to describe an ELS in the Bible. His four-letter example related to the traditional zero-point of the Hebrew calendar. Over the following centuries there are some hints that the ELS technique was known, but few definite examples have been found from before the middle of the 20th century. At this point many examples were found by the Slovak Rabbi Michael Ber Weissmandl and published by his students after his death in 1957. Nevertheless, the practice remained known only to a few until the early 1980s, when some discoveries of an Israeli school teacher Avraham Oren came to the attention of the mathematician Eliyahu Rips at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. Rips then took up the study together with his religious studies partners Doron Witztum and Alexander Rotenberg, and several others.
Rips and Witztum designed computer software for the ELS technique and subsequently found many examples. About 1985, they decided to carry out a formal test, and the "Great rabbis experiment" was born. This experiment tested the hypothesis that ELS's of the names of famous rabbinic personalities and their respective birth and death dates form a more compact arrangement than could be explained by chance. Their definition of "compact" was complex but, roughly, two ELSs were compactly arranged if they can be displayed together in a small window. When Rips et al. carried out the experiment, the data was measured and found to be statistically significant, supporting their hypothesis.
The "great rabbis experiment" went through several iterations, and was eventually published in 1994, in the peer-reviewed journal Statistical Science. Prior to publication, the journal's editor, Robert Kass, subjected the paper to three successive peer reviews by the journal's referees, who according to Kass were "baffled". Though still skeptical,[8] none of the reviewers had found any flaws. Understanding that the paper was certain to generate controversy, it was presented to readers in the context of a "challenging puzzle."
Witztum and Rips also performed other experiments, most of them successful, though none were published in journals. Another experiment, in which the names of the famous rabbis were matched against the places of their births and deaths (rather than the dates), was conducted in 1997 by Harold Gans, former Senior Cryptologic Mathematician for the United States National Security Agency.[9] Again, the results were interpreted as being meaningful and thus suggestive of a more than chance result.[10] These Bible codes became known to the public primarily due to the American journalist Michael Drosnin, whose book The Bible Code (Simon and Schuster, 1997) was a best-seller in many countries. Rips issued a public statement that he did not support Drosnin's work or conclusions;[11] even Gans has said that although the book states that the codes in the Torah can be used to predict future events: This is absolutely unfounded. There is no scientific or mathematical basis for such a statement, and the reasoning used to come to such a conclusion in the book is logically flawed.[12] In 2002, Drosnin published a second book on the same subject, called Bible Code II: the Countdown. The Jewish outreach group Aish-HaTorah employs Bible Codes in their Discovery Seminars to persuade secular Jews of the divinity of the Torah, and to encourage them to trust in its traditional Orthodox teachings. Use of Bible code techniques also spread into certain Christian circles, especially in the United States. The main early proponents were Yakov Rambsel, who is a Messianic Jew, and Grant Jeffrey. Another Bible code technique was developed in 1997 by Dean Coombs (also Christian). Various pictograms are claimed to be formed by words and sentences using ELS.[13]
Since 2000, physicist Nathan Jacobi, an agnostic Jew, and engineer Moshe Aharon Shak, an orthodox Jew, claim to have discovered hundreds of examples of lengthy, extended ELSs.[14] The number of extended ELSs at different lengths is compared with those expected from a non-encoded text, as determined by a formula from Markov chain theory.[15]
Criticism
The primary objection advanced against Bible codes is that information theory does not prohibit "noise" from appearing to be sometimes meaningful. Thus, if data chosen for ELS experiments are intentionally or unintentionally "cooked" before the experiment is defined, similar patterns can be found in texts other than the Torah. Although the probability of an ELS in a random place being a meaningful word is small, there are so many possible starting points and skip patterns that many such words can be expected to appear, depending on the details chosen for the experiment, and that it is possible to "tune" an ELS experiment to achieve a result which appears to exhibit patterns that overcome the level of noise.
Criticism of the original paper
In 1999, four authors, the Australian mathematician Brendan McKay, the Israeli mathematicians Dror Bar-Natan and Gil Kalai, and the Israeli psychologist Maya Bar-Hillel (collectively known as "MBBK") published a paper in Statistical Science, in which they argue that the case of Witztum, Rips and Rosenberg (WRR) is "fatally defective, indeed that their result merely reflects on the choices made in designing their experiment and collecting the data for it."[16] The MBBK paper was reviewed anonymously by four professional statisticians prior to publication. In the introduction to the paper, Robert Kass, the Editor of the Journal who previously had described the WRR paper as a "challenging puzzle" wrote that "considering the work of McKay, Bar-Natan, Kalai and Bar-Hillel as a whole it indeed appears, as they conclude, that the puzzle has been solved".[8]
In the MBBK paper, the authors present the following arguments:
- that because of problems in WRR's test method, the results of WRR's 1994 paper "may reflect (at least to some extent) uninteresting properties of the word list [the appellation-date word pairs] rather than an extraordinary property of Genesis,"[17] and that the test method used by WRR has properties that make it "exceptionally susceptible to systematic bias."[18]
- that WRR had many choices available when selecting the appellations, the dates, and the date forms.[19]
- that, despite the claims by WRR and S. Z. Havlin that Havlin prepared the appellations independently, the earliest available documents on the experiments do not state that the lists of appellations were prepared by an independent expert. Similarly, the authors quote a 1985 lecture by Eliyahu Rips, in which he describes the appellation selection process as taking "every possible variant that we considered reasonable", and makes no mention of Havlin or an independent expert.[20]
- that, by adding some appellations and removing some appellations from WRR's list 2, and then repeating the test on the initial 78,064 letters (the length of Genesis) of a Hebrew translation of War and Peace, they achieved a significance level of one in a million. The authors say this shows that "the freedom provided just in the selection of appellations is sufficient to explain the strong result" in WRR's 1994 paper.[21]
- The authors present a "study of variations", in which they repeated the experiments many times, each time making one or more minimal changes to the test method, the dates, or the date forms.[22] The authors conclude that "only a small fraction of variations made WRR's result stronger and then usually by only a small amount ... we believe that these observations are strong evidence for tuning ... "[23]
- The authors present experiments they conducted which they say show that some results of experiments by WRR and Harold Gans are "too good to be true." That is, some of the results are statistically improbable even if one accepts that WRR's hypothesis is true. The authors say that these studies "give support to the theory that WRR's experiments were tuned toward an overly idealized result consistent with the common expectations of statistically naïve researchers."[24]
- The authors present multiple experiments they conducted in which they attempted to replicate WRR's experiments. The authors used an independent expert to prepare the appellations and dates for each of these experiments. The authors report that the results of these attempted replications were negative.[25]
- that the available evidence indicates that the text of Genesis used by WRR is substantially different from its original form, and that ELSs with large skips (which WRR's experiments rely on) could not survive such changes.[26]
From these observations, MBBK created an alternative hypothesis to explain the "puzzle" of how the codes were discovered. MBBK's claim, in essence, was that the WRR authors had cheated[27][28] MBBK went on to describe the means by which the cheating might have occurred, and demonstrate the tactic as presumed.
MBBK's refutation was not strictly mathematical in nature, rather it asserted that the WRR authors and contributors had intentionally or unintentionally (a) selected the names and/or dates in advance and (b) designed their experiments to match their selection and thereby achieved their "desired" result. The MBBK paper argued that the ELS experiment is extraordinarily sensitive to very small changes in the spellings of appellations, and that the WRR result "merely reflects on the choices made in designing their experiment and collecting the data for it."
The MBBK paper demonstrated that this "tuning", when combined with what MBBK asserted was available "wiggle" room, was capable of generating a result similar to WRR's Genesis result in a Hebrew translation of War and Peace. Psychologist and MBBK co-author Maya Bar-Hillel subsequently summarized the MBBK view that the WRR paper was a hoax, an intentionally and a carefully designed "magic trick".[29]
The Bible codes (together with similar arguments concerning hidden prophecies in the writings of Shakespeare) have been quoted as examples of the Texas sharpshooter fallacy.
Replies to MBBK's criticisms
Harold Gans has argued that MBBK's hypothesis implies a conspiracy between WRR and their co-contributors to fraudulently tune the appellations in advance. Gans argues that the conspiracy must include Doron Witztum, Eliyahu Rips, and S. Z. Havlin, because all of them say that Havlin compiled the appellations independently. Gans argues further that such a conspiracy must include the multiple rabbis who have written a letter confirming the accuracy of Havlin's list. Finally, argues Gans, such a conspiracy must also include the multiple participants of the cities experiment conducted by Gans (which includes Gans himself). Gans concludes that "the number of people necessarily involved in [the conspiracy] will stretch the credulity of any reasonable person."[30]
Brendan McKay has replied that he and his colleagues have never accused Havlin or Gans of participating in a conspiracy. Instead, says McKay, Havlin likely did what WRR's early preprints said he did: he provided "valuable advices". Similarly, McKay accepts Gans' statements that Gans did not prepare the data for his cities experiment himself. McKay concludes that "there is only ONE person who needs to have been involved in knowing fakery, and a handful of his disciples who must be involved in the cover-up (perhaps with good intent)."[31]
The WRR authors issued a series of responses regarding of the claims of MBBK,[32] including the claim that no such tuning did or even could have taken place.[33] An earlier WRR response to a request by MBBK authors presented results from additional experiments that used the specific "alternate" name and date formats which MBBK suggested had been intentionally avoided by WRR.[34] Using MBBK's alternates, the results WRR returned showed equivalent or better support for the existence of the codes, and so challenged the "wiggle room" assertion of MBBK. In the wake of the WRR response, author Bar-Natan issued a formal statement of non-response.[35] After a series of exchanges with McKay and Bar-Hillel, WRR author Witztum responded in a new paper[36] claiming that McKay had used smoke screen tactics in creating several straw man arguments, and thereby avoided the points made by WRR authors refuting MBBK.[37] Witztum also claimed that, upon interviewing a key independent expert contracted by McKay for the MBBK paper, that some experiments performed for MBBK had validated, rather than refuted the original WRR findings, and questioned why MBBK had expunged these results from their paper. McKay replied to these claims.[38]
No publication in a peer reviewed scientific journal has appeared refuting MBBK's paper. In 2006, seven new Torah Codes papers were published at the 18th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR'06).
Robert Aumann, a notable game theorist and winner of the Nobel Prize in Economics in 2005, has followed the Bible Code research and controversy for many years. He wrote:[39] "Though the basic thesis of the research seems wildly improbable, for many years I thought that an ironclad case had been made for the codes; I did not see how 'cheating' could have been possible. Then came the work of the 'opponents' (see, for example, McKay, Bar-Natan, Bar-Hillel and Kalai, Statistical Science 14 (1999), 149–173). Though this work did not convince me that the data had been manipulated, it did convince me that it could have been; that manipulation was technically possible. "After a long and interesting analysis of the experiment and the dynamics of the controversy, stating for example that "almost everybody included [in the controversy] made up their mind early in the game" Aumann concluded:
"A priori, the thesis of the Codes research seems wildly improbable... Research conducted under my own supervision failed to confirm the existence of the codes – though it also did not establish their non-existence. So I must return to my a priori estimate, that the Codes phenomenon is improbable". [40]
Criticism of Michael Drosnin
Journalist Drosnin's books have been criticized by some who believe that the Bible Code is real but that it cannot predict the future.[41] On Drosnin's claim of Rabin's death, Drosnin wrote in his book "The Bible Code" (published in 1997) on page 120; "Yigal Amir could not be found in advance". This is very telling in that dangerous period of Israeli politics from the Oslo Accords of 1993 to the assassination of Yitzhak Rabin on November 4, 1995.[42] Critics have noted a huge error in the "code" Drosnin claimed to have found, they note Drosnin used the Biblical verse Deuteronomy 4:42. Scholars note; "For example, citing again the passage intersecting with Rabin: that passage is from Deuteronomy 4:42, but Drosnin ignores the words immediately following "a murderer who will murder." What comes next is the phrase "unwittingly" (biveli da'at). This is because the verse deals with the cities of refuge where accidental killers can find asylum. In this case, then, the message would refer to an accidental killing of (or by) Rabin and it would therefore be wrong. Another message (p. 71) supposedly contains a "complete" description of the terrorist bombing of a bus in Jerusalem on February 25, 1996. It includes the phrase "fire, great noise," but overlooks the fact that the letters which make up those two words are actually part of a larger phrase from Genesis 35:4 which says: "under the terebinth that was near Shechem." If the phrase does tell of a bus bombing, why not take it to indicate that it would be in Nablus, the site of ancient Shechem?" [43]
Drosnin also made a number of claims and alleged predictions that have since failed. Among the most important, Drosnin clearly states in his book "The Bible Code II", published on December 2, 2002, that there was to be a World War involving an "Atomic Holocaust" that would allegedly be the end of the world.[44] Another claim Drosnin makes in "The Bible Code II" is that the nation of Libya would develop weapons of mass destruction that they would then be given to terrorists who would then use them to attack the West (specifically the United States).[45] In reality Libya improved relations with the West in 2003 and gave up all their existing weapons of mass destruction programs.[46] A final claim Drosnin made in "The Bible Code II" was that Palestinian Authority leader Yasser Arafat would allegedly be assassinated by being shot to death by gunmen which Drosnin specifically stated would be from the Palestinian Hamas movement.[47] This prediction by Drosnin also failed, as Yasser Arafat died on November 11, 2004[48] of what was later declared to be natural causes (specifically a stroke brought on by an unknown infection).[49][50] The only conspiracy theories about Yasser Arafat allegedly being murdered have been made by a few Palestinian figures, and have involved alleged poisoning that was supposed to have been on the orders of Israeli officials. The only alleged Palestinian collaboration in this conspiracy theory involve two leading Palestinian figures from the Palestinian Fatah movement; those are current Palestinian Authority and Fatah leader Mahmoud Abbas and Mohammed Dahlan the former head of Fatah in Gaza.[51] Writer Randy Ingermanson criticized Drosnin by stating that; "And that's all they are, even for Drosnin – possibilities. He believes that the future is not fixed, and that the Bible code predicts all possible outcomes. Which makes it not much of a predictive tool, but again, he seems not to mind this very much. If you are laying bets based on Drosnin, you had better be willing to bet on all possible outcomes."[52]
Some accuse him of factual errors, claiming that he has much support in the scientific community,[53] mistranslating Hebrew words[54] to make his point more convincing, and using the Bible without proving that other books do not have similar codes.[55]
Responding to an explicit challenge from Drosnin, who claimed that other texts such as Moby-Dick would not yield ELS results comparable to the Torah, McKay created a new experiment that was tuned to find many ELS letter arrays in Moby-Dick that relate to modern events, including the assassination of Martin Luther King, Jr. He also found a code relating to the Rabin assassination, containing the assassin's first and last name and the university he attended, as well as the motive ("Oslo", relating to the Oslo accords).[56] Drosnin and others have responded to these claims, saying the tuning tactics employed by McKay were simply "nonsense", and providing analyses[57] to support their argument that the tables, data and methodologies McKay used to produce the Moby Dick results "simply do not qualify as code tables".[58] Matt Young writes in his analysis of these findings in Why Intelligent Design Fails, that despite the fact that all of the predictions found in Moby-Dick related to assassinations in the 20th century, that "the reason it looks amazing is that the number of possible things to look for, and the number of places to look, is much greater than you imagine."[59]
Skeptic Dave Thomas claimed to find other examples in many texts. While Thomas' methodology was alleged to have been refuted by Robert Haralick[60] and others, Thomas's criticisms were aimed at Drosnin, whose methodology was actually far worse. (In fact, Drosnin's example of "Clinton" in his first book violated the basic Bible Code concept of "Minimality"; Drosnin's "Clinton" was a completely invalid "code"). In addition, McKay claimed that Drosnin had used the flexibility of Hebrew orthography to his advantage, freely mixing classic (no vowels, Y and W strictly consonant) and modern (Y and W used to indicate i and u vowels) modes, as well as variances in spelling of K and T, to reach the desired meaning. In his television series John Safran vs God, Australian television personality John Safran and McKay again demonstrated the "tuning" technique, demonstrating that these techniques could produce "evidence" of the September 11 terrorist attacks on New York in the lyrics of Vanilla Ice's repertoire. Additionally, "coded" references in non-Torah Bible texts, as for instance the famous Number of the Beast, do not use the Bible code technique. And, the influence and consequences of scribal errors (e.g., misspellings, additions, deletions, misreadings, ...) are hard to account for in the context of a Bible coded message left secretly in the text. McKay and others claim that in the absence of an objective measure of quality and an objective way to select test subjects, it is not possible to positively determine whether any particular observation is significant or not. For that reason, most of the serious effort of the skeptics has been focused on the scientific claims of Witztum, Rips and Gans.
Other types of Bible codes
Another example of an alleged prediction coded in the text of the Bible, which is also attributed to Rabbi Chaim Michael Dov Weissmandl (who was mentioned above),[61] concerns the hanging of 10 Nazi leaders on October 16, 1946 following the Nuremberg Trials. Rabbi Weissmandl claimed that this event was predicted by the Biblical story about the hanging of the 10 sons of Haman, also as a final consequence of a (failed) genocidal plan against the Jews. The "coded" aspect of his speculation is that in the Masoretic text of the Bible, three letters within the list of Haman's sons are marked as small letters:[62] the tav ת of Parshandatha, the shin ש of Parmashtha and the zayin ז of Vajezatha. Rabbi Weissmandl pointed out that if you combine the three small letters together they form the word תשז, which in the accepted Hebrew notation for year numbers (using Gematria) corresponds to the Jewish year [5]707 Anno Mundi,[63] which is the Jewish year that the 10 Nazi leaders were executed (October 16, 1946 corresponds to Tishrei 21, 5707, the day known as Hoshanna Rabba, the day of severe judgments for the nations of the world, according to the Jewish calendar).[64][65] Many people criticize various aspects of this speculation.[66][67][68][69][70][71] They point out that there are several different traditions about what are the small letters in the names of Haman's sons. Also they point out that the proponents only mention the similarities between the cases, but ignore the many differences. More in general they point out that this is not exactly an a priori prediction, but rather a postdiction, and therefore the statistical significance of it, if there is any at all, cannot be reliably calculated.
See also
- Bibliomancy
- Confirmation bias
- Ergodic theory, which forms the foundation for modern information theory
- Gematria
- Pi (film)
- Quran code
- Ramsey theory, for an interesting and important notion of "unavoidable coincidences"
- Shemhamphorasch
- Theomatics
References
- ^ ["http://unitedisrael.org/blog/2009/11/" ""Bible Codes: Looking Back a Dozen Years""] Check
|url=value (help). - ^ Doron Witztum, Eliyahu Rips, Yoav Rosenberg (1994). "Equidistant letter sequences in the Book of Genesis". Statistical Science. 9 (3): 429–438. doi:10.1214/ss/1177010393.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ Shak, Moshe Aharon. 2004. Bible Codes Breakthrough. Montreal: Green Shoelace Books. 38
- ^ Haralick, Rips, and Glazerson. 2005. Torah Codes: A Glimpse into the Infinite. New York: Mazal & Bracha. 125
- ^ Sherman, R. Edwin, with Jacobi and Swaney. 2005. Bible Code Bombshell Green Forest, Ar.: New Leaf Press. 95–109
- ^ "Isaac Newton". JAH Publications.
- ^ "Bible Code". paranormality.com.
- ^ a b Kass, R. E. (1999). Introduction to "Solving the Bible Code Puzzle" by Brendan McKay, Dror Bar-Natan, Maya Bar-Hillel and Gil Kalai Statistical Science, 14. projecteuclid.org. p. 149.
- ^ "?".
- ^ http://www.torah-code.org/controversy/gans_statement.pdf
- ^ "Public Statement by Dr. Rips on Michael Drosnin's theories". despatch.cth.com.au.
- ^ http://www.skepdic.com/bibcode.html
- ^ "Bible Code Pictograms Bible Codes that form images that predict the future". bible-codes.org. Retrieved October 6, 2010.
- ^ "Find what you are looking for". biblecodedigest.com. Archived from the original on October 26 2010. Retrieved October 6, 2010. Unknown parameter
|deadurl=ignored (help); Check date values in:|archivedate=(help) - ^ Sherman, R. Edwin, with Jacobi and Swaney. 2005. Bible Code Bombshell Green Forest, Ar.: New Leaf Press. 281–286
- ^ B. McKay, D. Bar-Natan, M. Bar-Hillel, and G. Kalai (1999). Solving the Bible Code Puzzle. Statistical Science 14. projecteuclid.org. pp. 150–173.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ B. McKay, D. Bar-Natan, M. Bar-Hillel, and G. Kalai (1999). Solving the Bible Code Puzzle. Statistical Science, 14. projecteuclid.org. p. 154.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ B. McKay, D. Bar-Natan, M. Bar-Hillel, and G. Kalai (1999). Solving the Bible Code Puzzle. Statistical Science, 14. projecteuclid.org. p. 155.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ B. McKay, D. Bar-Natan, M. Bar-Hillel, and G. Kalai (1999). Solving the Bible Code Puzzle. Statistical Science, 14. projecteuclid.org. pp. 155–157.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ B. McKay, D. Bar-Natan, M. Bar-Hillel, and G. Kalai (1999). Solving the Bible Code Puzzle. Statistical Science, 14. projecteuclid.org. p. 156.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ B. McKay, D. Bar-Natan, M. Bar-Hillel, and G. Kalai (1999). Solving the Bible Code Puzzle. Statistical Science, 14. projecteuclid.org. p. 157.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ B. McKay, D. Bar-Natan, M. Bar-Hillel, and G. Kalai (1999). Solving the Bible Code Puzzle. Statistical Science, 14. projecteuclid.org. pp. 157–161, 168–171.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ B. McKay, D. Bar-Natan, M. Bar-Hillel, and G. Kalai (1999). Solving the Bible Code Puzzle. Statistical Science, 14. projecteuclid.org. p. 161.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ B. McKay, D. Bar-Natan, M. Bar-Hillel, and G. Kalai (1999). Solving the Bible Code Puzzle. Statistical Science, 14. projecteuclid.org. pp. 161–162.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ B. McKay, D. Bar-Natan, M. Bar-Hillel, and G. Kalai (1999). Solving the Bible Code Puzzle. Statistical Science, 14. projecteuclid.org. p. 164.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ B. McKay, D. Bar-Natan, M. Bar-Hillel, and G. Kalai (1999). Solving the Bible Code Puzzle. Statistical Science, 14. projecteuclid.org. pp. 165–166.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ "?".[dead link]
- ^ "This is not an html file just grab it". ma.huji.ac.il. Retrieved October 6, 2010.
- ^ Maya Bar-Hillel and Avishai Margali (December 1999). "Madness in the Method". dartmouth.edu. Retrieved October 6, 2010.
- ^ H. J. Gans. "A Primer on the Torah Codes Controversy for Laymen (part 1)". aish.com. Archived from the original on March 18 2008. Retrieved April 7, 2008. Unknown parameter
|deadurl=ignored (help); Check date values in:|archivedate=(help) - ^ B. McKay (2003). "Brief notes on Gans Primer". cs.anu.edu.au. Retrieved April 7, 2008.
- ^ "Refutations".
- ^ "No such tuning".
- ^ "Response".
- ^ "Non-response". Retrieved May 2, 2010.
- ^ "?".[dead link]
- ^ "?".[dead link]
- ^ "Concerning Witztum's response to our article "Codes in War and Peace – a reply to Doron Witztum"". Cs.anu.edu.au. June 15, 2001. Retrieved May 2, 2010.
- ^ "Analysis of the "Gans" Committee Report" (PDF). Retrieved May 2, 2010.
- ^ ^ Aumann, R.H., H. Furstenberg, I. Lapides, and D. Witztum (July 2004) (PDF). Analyses of the 'Gans' Committee Report (#365). Center for the Study of Rationality, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem. http://ratio.huji.ac.il/dp/dp_365.pdf. Retrieved 2006-06-20.
- ^ "The Bible Code". Leaderu.com. Retrieved May 2, 2010.
- ^ "Context of 'October 1995: Right-Wingers Call for Israeli Prime Minister Rabin's Death, Compare Israeli Government to Nazis'". Historycommons.org. Retrieved May 2, 2010.
- ^ "The Bible "Codes" – A Textual Perspective". Sas.upenn.edu. Archived from the original on May 15 2010. Retrieved 2010-05-02. Unknown parameter
|deadurl=ignored (help); Check date values in:|archivedate=(help) - ^ Drosnin, Michael (September 11, 2001). Bible Code II: The Countdown. Google Books. ISBN 978-0-14-200350-3. Retrieved May 2, 2010.
- ^ Drosnin, Michael (September 11, 2001). Bible Code II: The Countdown. Google Books. ISBN 978-0-14-200350-3. Retrieved May 2, 2010.
- ^ "Libya Gives Up Nuclear and Chemical Weapons". Commondreams.org. December 20, 2003. Retrieved May 2, 2010.
- ^ Drosnin, Michael (September 11, 2001). Bible Code II: The Countdown. Google Books. ISBN 978-0-14-200350-3. Retrieved May 2, 2010.
- ^ "Palestinian leader Arafat dies at 75". CNN. November 11, 2004. Archived from the original on June 01 2010. Retrieved April 26, 2010. Unknown parameter
|deadurl=ignored (help); Check date values in:|archivedate=(help) - ^ Erlanger, Steven; Altman, Lawrence K. (December 14, 2003). "Arafat died from stroke linked to infection, records show / Review finds poisoning unlikely, rebuts rumor that Palestinian leader had AIDS – SFGate". San Francisco Chronicle. Retrieved May 2, 2010.
- ^ Erlanger, Steven; Altman, Lawrence K. (September 8, 2005). "Medical Records Say Arafat Died From a Stroke". The New York Times. Retrieved April 26, 2010.
- ^ "The Muslim Brotherhood Official English Website". Ikhwanweb. Retrieved May 2, 2010.
- ^ "The Bible Code and Terrorism". Ingermanson.com. Retrieved May 2, 2010.
- ^ "Torah Codes". Cs.anu.edu.au. 2004-12-13. Archived from the original on April 18 2010. Retrieved 2010-05-02. Unknown parameter
|deadurl=ignored (help); Check date values in:|archivedate=(help) - ^ "Review of Michael Drosnin's Bible Code". Rsingermanson.com. Retrieved May 2, 2010.
- ^ "Barry Simon on Torah Codes". Wopr.com. September 8, 1998. Retrieved May 2, 2010.
- ^ "Assassinations Foretold in Moby Dick". Cs.anu.edu.au. Archived from the original on May 05 2010. Retrieved 2010-05-02. Unknown parameter
|deadurl=ignored (help); Check date values in:|archivedate=(help) - ^ Robert M. Haralick. "Skeptical About the Reasoning of the Bible Code Skeptic" (PDF). torah-code.org. Retrieved October 6, 2010.
- ^ "Can Anyone Beat George W. Bush in 2004?". CNN. Retrieved April 26, 2010.
- ^ "Matt Young, Taner Edis" ("2006"). "Why Intelligent Design Fails: A Scientific Critique of the New Creationism". "Rutgers University Press". p. "124". Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ^ Robert M. "Skeptical About the Reasoning of the Bible Code Skeptic" (PDF). torah-code.org. Retrieved October 6, 2010.
- ^ "I am statistically significant". torahone.com. Retrieved October 6, 2010.
- ^ "Small and Large Letters" in the: Jewish Encyclopedia, Funk and Wagnalls, New York 1901–1906. Volume 11, p. 411-412.
- ^ Using the Jewish method of recording years, the number 707 can represent the year 5707, this is the "minor era" system of notation of the Jewish year. For example, Webster's New World Hebrew Dictionary states: "In practice . . . the thousands are skipped and the Jewish year is referred to by quoting, in Jewish numerical symbols, the figure from the hundreds down" (p. xxiv, Introduction, The Jewish Calendar). See also chronogram.
- ^ "Hebrew Date Converter". hebcal.com. Retrieved October 6, 2010.
- ^ "Calendar Converter". calendarhome.com. Archived from the original on September 27 2010. Retrieved October 6, 2010. Unknown parameter
|deadurl=ignored (help); Check date values in:|archivedate=(help) - ^ Ephraim Rubin (August 9, 2002). "Purim 1946? Not Exactly". talkreason.org accessdate=October 6, 2010. Missing pipe in:
|publisher=(help) - ^ "Ralph the Sacred River". ralphriver.blogspot.com. March 28, 2005. Retrieved October 6, 2010.
- ^ "Purimfest 1946!!". dovbear.blogspot.com. March 24, 2005. Retrieved October 6, 2010.
- ^ R. D. Gold (2008). Bondage of the Mind: How Old Testament Fundamentalism Shackles the Mind and Enslaves the Spirit. Aldus Books. p. 71. ISBN 978-0-9796406-0-5.
- ^ "Genealogical Saga of Judaism (2001)". infidels.org. Archived from the original on September 28 2010. Retrieved October 6, 2010. Unknown parameter
|deadurl=ignored (help); Check date values in:|archivedate=(help) - ^ "Purim Fest, 1946 – A Tale of Kiruv". failedmessiah.typepad.com.
Notes
- Drosnin, Michael (1997). The Bible Code. USA: Simon & Schuster. ISBN 0-684-81079-4.
- Satinover, Jeffrey (1997). Cracking the Bible Code. New York: W. Morrow. ISBN 0-688-15463-8.
- Drosnin, Michael (1997). The Bible Code. UK: Weidenfeld & Nicolson. ISBN 0-297-81995-X.
- Drosnin, Michael (2002). The Bible Code II: The Countdown. USA: Viking Books. ISBN 0-670-03210-7.
- Drosnin, Michael (2002). The Bible Code II: The Countdown. UK: Weidenfeld & Nicolson. ISBN 0-297-84249-8.
- Drosnin, Michael (Forthcoming 2006). The Bible Code III: The Quest. UK: Weidenfeld & Nicolson. ISBN 0-297-84784-8. Check date values in:
|year=(help) - Stanton, Phil (1998). The Bible Code – Fact or Fake?. Wheaton, IL: Crossway Books. ISBN 0-89107-925-4.
- Haralick, Robert M.; Rips, Eliyahu; and Glazerson, Matiyahu (2005). Torah Codes: A Glimpse into the Infinite. Mazal & Bracha Publishing. ISBN 0-9740493-9-5.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
External links
- Notarikon Codes in the Bible according to Kabalah
- The Bible Code: Enigmas for Dummies – Do messages hidden within the Bible really predict the future? Skeptoid: Critical Analysis of Pop Phenomena
- The Bible Code, transcript of a story which aired on BBC Two, Thursday November 20, 2003, featuring comments by Drosnin, Rips, and McKay.
- Doron Witztum's codes page from Doron Witzum, a coauthor of the Statistical Sciences paper
- Tutorial Website from Professor Robert Haralick
- "Scientific Refutation of the Bible Codes" by Brendan McKay (Computer Science, Australian National University) and others
- The Bible Code: A Book Review by Allyn Jackson, plus Comments on the Bible Code by Shlomo Sternberg, Notices of the AMS September 1997 (see the American Mathematical Society)
- The Bible "Codes": a Textual Perspective, by Jeffrey H. Tigay (Near Eastern Languages and Civilizations, University of Pennsylvania)
- Madness in the Method, by Maya Bar-Hillel and Avishai Margalit, Chance, Dartmouth College
- Hidden Messages and The Bible Code from Committee for the Scientific Investigation of Claims of the Paranormal, publisher of Skeptical Inquirer Magazine
- Trying to stay objective, by Remy Wilders (Computer Science, France)