Kingdom of Aksum
Aksumite Empire መንግስቲ ኣኽሱም (Ge'ez) | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c. 100 AD – c. 940 AD | |||||||||||||||||||
Aksumite currency depicting King Endubis
| |||||||||||||||||||
 Axum kingdom circa 531CE | |||||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Aksum | ||||||||||||||||||
| Common languages | Ge'ez | ||||||||||||||||||
| Religion | (pre-Aksumite to 4th century) Judaism (before c. 330) Christianity (Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church; after c. 330) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||||||||||
| Negūs | |||||||||||||||||||
• c. 100 | Za Haqala (first known) | ||||||||||||||||||
• c. 940 | Dil Na'od (last) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Classical Antiquity to Early Middle Ages | ||||||||||||||||||
• Established | c. 100 AD | ||||||||||||||||||
• Conquest by Gudit | c. 960 AD | ||||||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||||||
| 350[1] | 1,250,000 km2 (480,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Currency | Aksumite currency | ||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Today part of | Eritrea Ethiopia Djibouti Sudan , for a period also covered small part of Yemen | ||||||||||||||||||
Part of a series on the |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History of Ethiopia | ||||||||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Early history
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Middle Ages
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Early modern history
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Modern history
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Recent history
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Topics |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Part of a series on the |
|---|
| History of Eritrea |
|
Post-Colonial |
|
|
The Kingdom of Aksum (Ge'ez: መንግስቲ ኣኽሱም), also known as the Kingdom of Axum or the Aksumite Empire, was an ancient kingdom centered in what is now Eritrea and the Tigray Region of northern Ethiopia.[2][3] Axumite Emperors were powerful sovereigns, styling themselves King of kings, king of Aksum, Himyar, Raydan, Saba, Salhen, Tsiyamo, Beja and of Kush.[4] Ruled by the Aksumites, it existed from approximately 80 BC to AD 825.[5] The polity was centered in the city of Axum and grew from the proto-Aksumite Iron Age period around the 4th century BC to achieve prominence by the 1st century AD. Aksum became a major player on the commercial route between the Roman Empire and Ancient India. The Aksumite rulers facilitated trade by minting their own Aksumite currency, with the state establishing its hegemony over the declining Kingdom of Kush. It also regularly entered the politics of the kingdoms on the Arabian Peninsula and eventually extended its rule over the region with the conquest of the Himyarite Kingdom. The Manichaei prophet Mani (died 274 AD) regarded Axum as one of the four great powers of his time, the others being Persia, Rome, and China.[2][6][7] [8]
The Aksumites erected monumental stelae, which served a religious purpose in pre-Christian times. One of these granite columns is the largest such structure in the world, at 90 feet.[9] Under Ezana (fl. 320–360) Aksum adopted Christianity. In the 7th century, early Muslims from Mecca sought refuge from Quraysh persecution by travelling to the kingdom, a journey known in Islamic history as the First Hijra.[10][11]
The kingdom's ancient capital, also called Axum, is now a town in Tigray Region (northern Ethiopia). The Kingdom used the name "Ethiopia" as early as the 4th century.[12][13] Tradition claims Axum as the alleged resting place of the Ark of the Covenant and the purported home of the Queen of Sheba.[14]
Historical records[edit]
Aksum is mentioned in the first-century AD Periplus of the Erythraean Sea as an important market place for the trade in ivory, which was exported throughout the ancient world. It states that the ruler of Aksum in the first century was Zoskales, who, besides ruling the kingdom, likewise controlled land near the Red Sea: Adulis (near Massawa) and lands through the highlands of present-day Eritrea. He is also said to have been familiar with Greek literature.
4. Below Ptolemais of the Hunts, at a distance of about three thousand stadia, there is Adulis, a port established by law, lying at the inner end of a bay that runs in toward the south. Before the harbor lies the so-called Mountain Island, about two hundred stadia seaward from the very head of the bay, with the shores of the mainland close to it on both sides. Ships bound for this port now anchor here because of attacks from the land. They used formerly to anchor at the very head of the bay, by an island called Diodorus, close to the shore, which could be reached on foot from the land; by which means the barbarous natives attacked the island. Opposite Mountain Island, on the mainland twenty stadia from shore, lies Adulis, a fair-sized village, from which there is a three-days' journey to Coloe, an inland town and the first market for ivory. From that place to the city of the people called Auxumites there is a five days' journey more; to that place all the ivory is brought from the country beyond the Nile through the district called Cyeneum, and thence to Adulis. Practically the whole number of elephants and rhinoceros that are killed live in the places inland, although at rare intervals they are hunted on the seacoast even near Adulis. Before the harbor of that market-town, out at sea on the right hand, there lie a great many little sandy islands called Alalaei, yielding tortoise-shell, which is brought to market there by the Fish-Eaters.
...
6. There are imported into these places, undressed cloth made in Egypt for the Berbers; robes from Arsinoe; cloaks of poor quality dyed in colors; double-fringed linen mantles; many articles of flint glass, and others of murrhine, made in Diospolis; and brass, which is used for ornament and in cut pieces instead of coin; sheets of soft copper, used for cooking-utensils and cut up for bracelets and anklets for the women; iron, which is made into spears used against the elephants and other wild beasts, and in their wars. Besides these, small axes are imported, and adzes and swords; copper drinking-cups, round and large; a little coin for those coming to the market; wine of Laodicea and Italy, not much; olive oil, not much; for the king, gold and silver plate made after the fashion of the country, and for clothing, military cloaks, and thin coats of skin, of no great value. Likewise from the district of Ariaca across this sea, there are imported Indian iron, and steel, and Indian cotton cloth; the broad cloth called monache and that called sagmatogene, and girdles, and coats of skin and mallow-colored cloth, and a few muslins, and colored lac. There are exported from these places ivory, and tortoiseshell and rhinoceros-horn. The most from Egypt is brought to this market from the month of January to September, that is, from Tybi to Thoth; but seasonably they put to sea about the month of September.[15]
History[edit]
Origins[edit]
Largely on the basis of Carlo Conti Rossini's theories and prolific work on Ethiopian history, Aksum was previously thought to have been founded by the Sabaeans, who spoke a language from the Semitic branch of the Afroasiatic language family. Evidence suggests that Semitic-speaking Aksumites semiticized the Agaw people, who originally spoke other Afroasiatic languages from the family's Cushitic branch, and had already established an independent civilization in the territory before the arrival of the Sabaeans.[12][a][16]
Scholars like Stuart Munro-Hay thus point to the existence of an older kingdom known as Dʿmt, which flourished in the area between the tenth and fifth centuries BC, prior to the proposed Sabaean migration in the fourth or fifth century BC. They also cite evidence indicating that Sabaean settlers resided in the region for little more than a few decades.[12] Sabaean influence is now thought to have been minor, limited to a few localities, and disappearing after a few decades or a century, perhaps representing a trading or military colony in some sort of symbiosis or military alliance with the civilization of D'mt or some proto-Aksumite state.[12] As George Hatke put it:
The most significant and lasting impact of these colonists was the establishment of a writing system and the introduction of Semitic speech—both of which the Ethiopians modified considerably. . . . South Arabian culture [was] a foreign commodity from which the Ethiopians were able to freely pick and chose when they saw fit, rather than an entire civilization imposed by foreign rulers.[17]
The Ge'ez language is no longer universally thought of, as previously assumed, to be an offshoot of Sabaean or Old South Arabian,[18] and there is some linguistic (though not written) evidence of Semitic languages being spoken in Eritrea and Ethiopia since approximately 2000 BC.[19] However, the Ge'ez script later replaced Epigraphic South Arabian in the Kingdom of Aksum.

Empire[edit]


The Kingdom of Aksum was a trading empire centered in Eritrea and northern Ethiopia.[21] It existed approximately 100–940 AD, growing from the Iron Age proto-Aksumite period c. fourth century BC to achieve prominence by the first century AD.
According to the Book of Aksum, Aksum's first capital, Mazaber, was built by Itiyopis, son of Cush.[22] The capital was later moved to Axum in northern Ethiopia. The Kingdom used the name "Ethiopia" as early as the fourth century.[12][23]
The Empire of Aksum at its height at times extended across most of present-day Eritrea, Ethiopia, Somalia, Djibouti, Sudan, Yemen and Saudi Arabia. The capital city of the empire was Aksum, now in northern Ethiopia. Today a smaller community, the city of Aksum was once a bustling metropolis, cultural and economic center. Two hills and two streams lie on the east and west expanses of the city; perhaps providing the initial impetus for settling this area. Along the hills and plain outside the city, the Aksumites had cemeteries with elaborate grave stones called stelee or obelisks. Other important cities included Yeha, Hawulti-Melazo, Matara, Adulis, and Qohaito, the last three of which are now in Eritrea. By the reign of Endubis in the late third century, it had begun minting its own currency and was named by Mani as one of the four great powers of his time along with the Sasanian Empire, Roman Empire, and "Three Kingdoms" China. The Aksumites adopted Christianity as its state religion in 325 or 328 under King Ezana, and was the first state ever to use the image of the cross on its coins.[24][25]
Around the 3rd century (possibly c.240–c.260), the Axumites led by Sembrouthes were victorious over the Sesea with Sesea becoming a tributary of the Kingdom of Aksum.[26][27]
Around 330 AD, Ezana of Axum led his army into the Kingdom of Meroë, conquering and sacking the town itself. A large stone monument was left there, and the conquest is also related on Ezana Stone.[28]
Around 520, King Kaleb sent an expedition to Yemen against the Jewish Himyarite king Dhu Nuwas, who was persecuting the Christian community there. For nearly half a century south Arabia would become an Ethiopian protectorate under Abraha and his son Masruq[29]
Dhu Nuwas was deposed and killed and Kaleb appointed a Christian Himyarite, Esimiphaios ("Sumuafa Ashawa"), as his viceroy. However, around 525 this viceroy was deposed by the Aksumite general Abraha with support of Ethiopians who had settled in Yemen, and withheld tribute to Kaleb. When Kaleb sent another expedition against Abraha this force defected, killing their commander, and joining Abraha. Another expedition sent against them was defeated, leaving Yemen under Abraha's rule, although payment of a tribute resumed, where he continued to promote the Christian faith until his death.
After Abraha's death, his son Masruq Abraha continued the Axumite vice-royalty in Yemen, resuming payment of tribute to Axum. However, his half-brother Ma'd-Karib revolted. After being denied by Justinian, Ma'd-Karib sought help from Khosrow I, the Sassanid Persian Emperor, thus triggering the Aksumite–Persian wars.
Khosrow who sent a small fleet and army under commander Vahrez to depose the current king of Yemen. The war culminated with the Siege of Sana'a, capital of Axumite Yemen. After its fall in 570, and Masruq death, Ma'd-Karib's son, Saif, was put on the throne. In 575, the war resumed again, after Saif was killed by Axumites. The Persian general Vahrez led another army of 8000, ending Axum rule in Yemen and becoming hereditary governor of Yemen.
According to Munro-Hay, these wars may have been Aksum's swan-song as a great power, with an overall weakening of Aksumite authority and over-expenditure in money and manpower.
According to Ethiopian traditions, Kaleb eventually abdicated and retired to a monastery. It is also possible that Ethiopia was affected by the Plague of Justinian around this time.[12]

Aksum, though weakened, remained a strong empire and trading power until the rise of Islam in the 7th century. However, unlike the relations between the Islamic powers and Christian Europe, Aksum (see Sahama), was on good terms with its Islamic neighbors and provided shelter to Muhammad's early followers around 615.[2][6] Nevertheless, as early as 640, Umar sent a naval expedition against Adulis, the Expedition of Alqammah bin Mujazziz, but it was eventually defeated.[30]
Aksumite naval power also declined throughout the period, though in 702 Aksumite pirates were able to invade the Hejaz and occupy Jeddah. In retaliation, however, Sulayman ibn Abd al-Malik was able to take the Dahlak Archipelago from Aksum, which became Muslim from that point on, though it later recovered in the ninth century and became a vassal to the Emperor of Ethiopia.[31]
Decline[edit]
Eventually, the Rashidun Caliphate took control of the Red Sea and Egypt by 646 AD/CE, pushing Aksum into economic isolation. Northwest of Aksum, in modern-day Sudan, the Christian states of Nobatia, Makuria and Alodia lasted till the 13th century before becoming Islamic. Aksum, isolated, nonetheless still remained Christian.[12]
After a second golden age in the early 6th century[12] the empire began to decline in the mid 6th century,[32] eventually ceasing its production of coins in the early 7th century. Around this same time, the Aksumite population was forced to go farther inland to the highlands for protection, abandoning Aksum as the capital. Arab writers of the time continued to describe Ethiopia (no longer referred to as Aksum) as an extensive and powerful state, though they had lost control of most of the coast and their tributaries. While land was lost in the north, it was gained in the south; and, though Ethiopia was no longer an economic power, it still attracted Arab merchants. The capital was moved to a new location, currently unknown, though it may have been called Ku'bar or Jarmi.[12]
Under the reign of Degna Djan, during the 10th century, the empire kept expanding south, and sent troops into the modern-day region of Kaffa,[33] while at the same time undertaking missionary activity into Angot and Amhara.
Local history holds that, around 960, a Jewish Queen named Yodit (Judith) or "Gudit" defeated the empire and burned its churches and literature. While there is evidence of churches being burned and an invasion around this time, her existence has been questioned by some modern authors. Another possibility is that the Aksumite power was ended by a southern pagan queen named Bani al-Hamwiyah, possibly of the tribe al-Damutah or Damoti (Sidama). It is clear from contemporary sources that a female usurper did indeed rule the country at this time, and that her reign ended some time before 1003. After a short Dark Age, the Aksumite Empire was succeeded by the Agaw Zagwe dynasty in the 11th or 12th century (most likely around 1137), although limited in size and scope. However, Yekuno Amlak, who killed the last Zagwe king and founded the modern Solomonic dynasty around 1270 traced his ancestry and his right to rule from the last emperor of Aksum, Dil Na'od. It should be mentioned that the end of the Aksumite Empire didn't mean the end of Aksumite culture and traditions; for example, the architecture of the Zagwe dynasty at Lalibela and Yemrehana Krestos Church shows heavy Aksumite influence.[12]
Other reasons for the decline are more scientific in nature. Climatic change and trade isolation are probably also large reasons for the decline of the culture.[citation needed] The local subsistence base was substantially augmented by a climatic shift during the 1st century AD that reinforced the spring rains, extended the rainy season from 3 1/2 to six or seven months, vastly improved the surface and subsurface water supply, doubled the length of the growing season, and created an environment comparable to that of modern central Ethiopia (where two crops can be grown per annum without the aid of irrigation). This appears to explain how one of the marginal agricultural environments of Ethiopia was able to support the demographic base that made this far flung commercial empire possible. It may also explain why no Aksumite rural settlement expansion into the moister, more fertile, and naturally productive lands of Begemder or Lasta can be verified during the heyday of Aksumite power. As international profits from the exchange network declined, Aksum lost its ability to control its own raw material sources and that network collapsed. The already persistent environmental pressure of a large population to maintain a high level of regional food production had to be intensified. The result was a wave of soil erosion that began on a local scale c. 650 and attained catastrophic proportions after 700. Presumably complex socio-economic inputs compounded the problem. These are traditionally reflected in declining maintenance, deterioration and partial abandonment of marginal crop land, shifts to destructive pastoral exploitation, and eventual, wholesale and irreversible land degradation. This syndrome was possibly accelerated by an apparent decline in rainfall reliability beginning 730–760, with the presumed result that an abbreviated modern growing season was reestablished during the 9th century.[34]
Foreign relations, trade, and economy[edit]
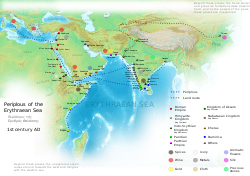

Covering parts of what is now northern Ethiopia and southern and eastern Eritrea, Aksum was deeply involved in the trade network between India and the Mediterranean (Rome, later Byzantium), exporting ivory, tortoise shell, gold and emeralds, and importing silk and spices.[2][6] Aksum's access to both the Red Sea and the Upper Nile enabled its strong navy to profit in trade between various African (Nubia), Arabian (Yemen), and Indian states.
The main exports of Aksum were, as would be expected of a state during this time, agricultural products. The land was much more fertile during the time of the Aksumites than now, and their principal crops were grains such as wheat and barley. The people of Aksum also raised cattle, sheep, and camels. Wild animals were also hunted for things such as ivory and rhinoceros horns. They traded with Roman traders as well as with Egyptian and Persian merchants. The empire was also rich with gold and iron deposits. These metals were valuable to trade, but another mineral was also widely traded: salt. Salt was abundant in Aksum and was traded quite frequently.[35][11]
It benefited from a major transformation of the maritime trading system that linked the Roman Empire and India. This change took place around the start of the 1st century. The older trading system involved coastal sailing and many intermediary ports. The Red Sea was of secondary importance to the Persian Gulf and overland connections to the Levant. Starting around 100 BC a route from Egypt to India was established, making use of the Red Sea and using monsoon winds to cross the Arabian Sea directly to southern India. By about 100 AD, the volume of traffic being shipped on this route had eclipsed older routes. Roman demand for goods from southern India increased dramatically, resulting in greater number of large ships sailing down the Red Sea from Roman Egypt to the Arabian Sea and India.[36][37]

The Kingdom of Aksum was ideally located to take advantage of the new trading situation. Adulis soon became the main port for the export of African goods, such as ivory, incense, gold, slaves, and exotic animals. In order to supply such goods the kings of Aksum worked to develop and expand an inland trading network. A rival, and much older trading network that tapped the same interior region of Africa was that of the Kingdom of Kush, which had long supplied Egypt with African goods via the Nile corridor. By the 1st century AD, however, Aksum had gained control over territory previously Kushite. The Periplus of the Erythraean Sea explicitly describes how ivory collected in Kushite territory was being exported through the port of Adulis instead of being taken to Meroë, the capital of Kush. During the 2nd and 3rd centuries AD the Kingdom of Aksum continued to expand their control of the southern Red Sea basin. A caravan route to Egypt was established which bypassed the Nile corridor entirely. Aksum succeeded in becoming the principal supplier of African goods to the Roman Empire, not least as a result of the transformed Indian Ocean trading system.[39]
Society[edit]
The Aksumite population consisted of Semitic-speaking people (collectively known as Habeshas),[40][41][42] Cushitic-speaking people, and Nilo-Saharan-speaking people (the Kunama and Nara).
Aksumites had a modified feudal system to farm the land.[24][25]
Kings[edit]
The Aksumite kings had the official title ነገሠ ፡ ነገሠተ ngś ngśt - King of Kings (later vocalization Ge'ez ንጉሠ ፡ ነገሥት nigūśa nagaśt, Modern Ethiosemitic nigūse negest).
Culture[edit]
The Empire of Aksum is notable for a number of achievements, such as its own alphabet, the Ge'ez script which was eventually modified to include vowels, becoming an abugida. Furthermore, in the early times of the empire, around 1700 years ago, giant Obelisks to mark emperors' (and nobles') tombs (underground grave chambers) were constructed, the most famous of which is the Obelisk of Aksum.
Under Emperor Ezana, Aksum adopted Christianity in place of its former polytheistic and Judaic religions around 325. This gave rise to the present day Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church (only granted autonomy from the Coptic Church in 1959), and Eritrean Orthodox Tewahdo Church (granted autonomy from the Ethiopian Orthodox church in 1993). Since the schism with Orthodoxy following the Council of Chalcedon (451), it has been an important Miaphysite church, and its scriptures and liturgy continue to be in Ge'ez.[2][6]
Religion[edit]

Before its conversion to Christianity, the Aksumites practiced a polytheistic religion related to the religion practiced in southern Arabia. This included the use of the crescent-and-disc symbol used in southern Arabia and the northern horn.[43] In the UNESCO sponsored General History of Africa French archaeologist Francis Anfray, suggests that the pagan Aksumites worshipped Astar, his son, Mahrem, and Beher.[44]

Steve Kaplan argues that with Aksumite culture came a major change in religion, with only Astar remaining of the old gods, the others being replaced by what he calls a "triad of indigenous divinities, Mahrem, Beher and Medr." He also suggests that Aksum culture was significantly influenced by Judaism, saying that "The first carriers of Judaism reached Ethiopia between the reign of Queen of Sheba BC and conversion to Christianity of King Ezana in the fourth century AC." He believes that although Ethiopian tradition suggests that these were present in large numbers, that "A relatively small number of texts and individuals dwelling in the cultural, economic, and political center could have had a considerable impact." and that "their influence was diffused throughout Ethiopian culture in its formative period. By the time Christianity took hold in the fourth century, many of the originally Hebraic-Jewish elements had been adopted by much of the indigenous population and were no longer viewed as foreign characteristics. Nor were they perceived as in conflict with the acceptance of Christianity."[45]
Before converting to Christianity King Ezana II's coins and inscriptions show that he might have worshiped the gods Astar, Beher, Meder/Medr, and Mahrem. Another of Ezana's inscriptions is clearly Christian and refers to "the Father, the Son, and the Holy Spirit".[46] Around 324 AD the King Ezana II was converted to Christianity by his teacher Frumentius, the founder of the Ethiopian Orthodox Church.[47][11] Frumentius taught the emperor while he was young, and it is believed that at some point staged the conversion of the empire.[36][37] We know that the Aksumites converted to Christianity because in their coins they replaced the disc and crescent with the cross. Frumentius was in contact with the Church of Alexandria, and was appointed Bishop of Ethiopia around the year 330. The Church of Alexandria never closely managed the affairs of the churches in Aksum, allowing them to develop their own unique form of Christianity.[24][25] However, the Church of Alexandria probably did retain some influence considering that the churches of Aksum followed the Church of Alexandria into Oriental Orthodoxy by rejecting the Fourth Ecumenical Council of Chalcedon.[48] Aksum is also the alleged home of the holy relic the Ark of the Covenant. The Ark is said to have been placed in the Church of Our Lady Mary of Zion by Menelik I for safekeeping.[2][6] Islam came in the 7th century at the reign of Ashama ibn-Abjar when the followers of the Prophet Muhammed were persecuted by the ruling tribe and begun migrating, after the first followers got asylum from the King many begun to migrate. Many returned to Medina in 622, but there were exiled Arabs who stayed and some even converted to the Ethiopian Orthodox Church.
Ethiopian sources[edit]
Ethiopian sources such as the Kebra Nagast and the Fetha Nagast[49][11] describe Aksum as a Jewish Kingdom. The Kebra Nagast contains a narrative of how the Queen of Sheba/Queen Makeda of Ethiopia met King Solomon and traces Ethiopia's to Menelik I, her son by King Solomon of Israel. In its existing form the Kebra Nagast is at least 700 years old and is considered by the Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church to be a reliable and historic work.
Coinage[edit]

The Empire of Aksum was one of the first African polities economically and politically ambitious enough to issue its own coins,[36][37] which bore legends in Ge'ez and Greek. From the reign of Endubis up to Armah (approximately 270 to 610), gold, silver and bronze coins were minted. Issuing coinage in ancient times was an act of great importance in itself, for it proclaimed that the Aksumite Empire considered itself equal to its neighbors. Many of the coins are used as signposts about what was happening when they were minted. An example being the addition of the cross to the coin after the conversion of the empire to Christianity. The presence of coins also simplified trade, and was at once a useful instrument of propaganda and a source of profit to the empire.
Architecture[edit]
Homely architecture[edit]
In general, elite Aksumite buildings such as palaces were constructed atop podia built of loose stones held together with mud-mortar, with carefully cut granite corner blocks which rebated back a few centimeters at regular intervals as the wall got higher, so the walls narrowed as they rose higher. These podia are often all that survive of Aksumite ruins. Above the podia, walls were generally build with alternating layers of loose stone (often whitewashed, like at Yemrehana Krestos Church) and horizontal wooden beams, with smaller round wooden beams set in the stonework often projecting out of the walls (these are called 'monkey heads') on the exterior and sometimes the interior. Both the podia and the walls above exhibited no long straight stretches, but were indented at regular intervals so that any long walls consisted of a series of recesses and salients. This helped to strengthen the walls. Worked granite was used for architectural features including columns, bases, capitals, doors, windows, paving, water spouts (often shaped like lion heads) and so on, as well as enormous flights of stairs that often flanked the walls of palace pavilions on several sides. Doors and windows were usually framed by stone or wooden cross-members, linked at the corners by square 'monkey heads', though simple lintels were also used. Many of these Aksumite features are seen carved into the famous stelae as well as in the later rock hewn churches of Tigray and Lalibela.[12]
Palaces usually consisted of a central pavilion surrounded by subsidiary structures pierced by doors and gates that provided some privacy (see Dungur for an example). The largest of these structures now known is the Ta'akha Maryam, which measured 120 × 80m, though as its pavilion was smaller than others discovered it is likely that others were even larger.[12]
Some clay models of houses survive to give us an idea of what smaller dwellings were like. One depicts a round hut with a conical roof thatched in layers, while another depicts a rectangular house with rectangular doors and windows, a roof supported by beams that end in 'monkey heads', and a parapet and water spout on the roof. Both were found in Hawelti. Another depicts a square house with what appear to be layers of pitched thatch forming the roof.[12]
Stelae[edit]
The stelae (hawilt/hawilti in local languages) are perhaps the most identifiable part of the Aksumite architectural legacy. These stone towers served to mark graves and represent a magnificent multi-storied palace. They are decorated with false doors and windows in typical Aksumite design. The largest of these towering obelisks would measure 33 meters high had it not fractured. The Stelae have most of their mass out of the ground, but are stabilized by massive underground counter-weights. The stone was often engraved with a pattern or emblem denoting the king's or the noble's rank.[24][25]
In literature[edit]
The Aksumite Empire is portrayed as the main ally of Byzantium in the Belisarius series by David Drake and Eric Flint published by Baen Books. The series takes place during the reign of Kaleb, who in the series was assassinated by the Malwa in 532 at the Ta'akha Maryam and succeeded by his youngest son Eon bisi Dakuen.
In the Elizabeth Wein series The Lion Hunters, Mordred and his family take refuge in Aksum after the fall of Camelot. Kaleb is the ruler in the first book; he passes his sovereignty onto his son Gebre Meskal, who rules during the Plague of Justinian.
The Book of Enoch, a pre-Christian work is written in Ge'ez - the written language of Aksum.[50]
Gallery[edit]
The Obelisk of Aksum after being returned to Ethiopia.
See also[edit]
Notes[edit]
- ^ Munro-Hays explains, "Evidently the arrival of Sabaean influences does not represent the beginning of Ethiopian civilisation.... Semiticized Agaw peoples are thought to have migrated from south-eastern Eritrea possibly as early as 2000 BC, bringing their 'proto-Ethiopic' language, ancestor of Ge'ez and the other Ethiopian Semitic languages, with them; and these and other groups had already developed specific cultural and linguistic identities by the time any Sabaean influences arrived."[12]
References[edit]
- ^ Turchin, Peter and Jonathan M. Adams and Thomas D. Hall: "East-West Orientation of Historical Empires and Modern States", p. 222. Journal of World-Systems Research, Vol. XII, No. II, 2006
- ^ a b c d e f The wealth of Africa – The kingdom of Aksum – Teachers’ notes britishmuseum.org
- ^ Butzer, Karl W. (1981). "Rise and Fall of Axum, Ethiopia: A Geo-Archaeological Interpretation". American Antiquity. Cambridge University Press. 46 (3): 471–495. doi:10.2307/280596. JSTOR 280596.
- ^ Dr. Stuart Munro-Hay, [1] Aksum: An African Civilisation of Late Antiquity. Chap. 11, Inscription DAE 8
- ^ Hunt, Katie. "Archeologists unearth lost town from little-known ancient East African empire". CNN. Retrieved 2019-12-12.
- ^ a b c d e Daily Life in Aksum eduplace.com
- ^ Marshall, Michael. "Lost Ethiopian town comes from an ancient empire that rivalled Rome". New Scientist. Retrieved 2019-12-10.
- ^ Harrower, Michael J.; Dumitru, Ioana A.; Perlingieri, Cinzia; Nathan, Smiti; Zerue, Kifle; Lamont, Jessica L.; Bausi, Alessandro; Swerida, Jennifer L.; Bongers, Jacob L.; Woldekiros, Helina S.; Poolman, Laurel A. (December 2019). "Beta Samati: discovery and excavation of an Aksumite town". Antiquity. 93 (372): 1534–1552. doi:10.15184/aqy.2019.84. ISSN 0003-598X.
- ^ Brockman, Norbert (2011). Encyclopedia of Sacred Places, Volume 1. ABC-CLIO. p. 30. ISBN 978-1598846546.
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-01-07. Retrieved 2017-01-06.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ a b c d http://goblues.org/faculty/weekse/files/2012/08/axum-and-the-solomonic-dynasty.pdf
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Munro-Hay, Stuart (1991). Aksum: An African Civilization of Late Antiquity (PDF). Edinburgh: University Press. p. 57. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 23, 2013. Retrieved February 1, 2013.
- ^ Paul B. Henze, Layers of Time: A History of Ethiopia, 2005.
- ^ Raffaele, Paul (December 2007). "Keepers of the Lost Ark?". Smithsonian Magazine. Retrieved 5 April 2011.
- ^ "The Periplus of the Erythraean Sea: Travel and Trade in the Indian Ocean by a Merchant of the First Century". Fordham University Internet History Sourcebooks., chapters 4 and 5
- ^ Pankhurst, Richard K. P. (January 17, 2003). "Let's Look Across the Red Sea I". Addis Tribune. Archived from the original on January 9, 2006. Retrieved February 1, 2013.
- ^ George Hatke, “Africans in Arabia Felix: Aksumite Relations with Himyar in the Sixth Century” (PhD diss., Princeton University, 2011).
- ^ Weninger, Stefan, "Ge'ez" in Encyclopaedia Aethiopica: D-Ha, p. 732.
- ^ Stuart, Munro-Hay (1991). Aksum: An African Civilization of Late Antiquity. Edinburgh: University Press. p. 57. ISBN 978-0-7486-0106-6.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
metwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Phillipson, David (2012). Neil Asher Silberman (ed.). The Oxford Companion to Archaeology. Oxford University Press. p. 48.
- ^ Africa Geoscience Review. Rock View International. 2003-01-01. p. 366.
- ^ Henze, Paul B. (2005) Layers of Time: A History of Ethiopia, ISBN 1-85065-522-7.
- ^ a b c d http://users.clas.ufl.edu/sterk/junsem/haas.pdf
- ^ a b c d http://whc.unesco.org/en/list/15
- ^ Thonemann, Peter (2013), "Phrygia: an anarchist history, 950 BC–AD 100", Roman Phrygia, Cambridge University Press, pp. 1–40, doi:10.1017/cbo9781139381574.002, ISBN 978-1-139-38157-4
- ^ "The Christian Topography of Cosmas Indicopleustes". Nature. 84 (2127): 133–134. August 1910. Bibcode:1910Natur..84..133.. doi:10.1038/084133a0. hdl:2027/coo1.ark:/13960/t07w6zm1b. ISSN 0028-0836.
- ^ Stanley M. Burstein, "Axum and the Fall of Meroe, Journal of the American Research Center in Egypt Vol. 18 (1981), pp. 47–50
- ^ electricpulp.com. "ABNĀʾ – Encyclopaedia Iranica". www.iranicaonline.org. Retrieved 2018-04-13.
- ^ E. Cerulli, "Ethiopia's Relations with the Muslim World" in Cambridge History of Africa: Africa from the Seventh to the Eleventh century, p. 575; Trimingham, Spencer, Islam in Ethiopia, p. 46.
- ^ Daniel Kendie, The Five Dimensions of the Eritrean Conflict 1941–2004: Deciphering the Geo-Political Puzzle. United States of America: Signature Book Printing, Inc., 2005, pp. 228.
- ^ David W. Phillipson (2012): Foundations of an African Civilisation: Aksum and the Northern Horn, 1000 BC – AD 1300. James Currey. p. 209
- ^ Werner J. Lange, ”History of the Southern Gonga (southwestern Ethiopia)“, Steiner, 1982, p. 18
- ^ Karl W. Butzer, ”Rise and Fall of Axum, Ethiopia: A Geo-Archaeological Interpretation“, American Antiquity 46, (July 1981), p. 495
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-01-07. Retrieved 2017-01-06.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ a b c http://www.ruperthopkins.com/pdf/Kingdom_of_Axum.pdf
- ^ a b c "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-01-07. Retrieved 2017-01-06.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ De Lorenzi, James (2015), Guardians of the Tradition: Historians and Historical Writing in Ethiopia and Eritrea, Rochester: University of Rochester Press, pp. 15–16, ISBN 978-1-58046-519-9.
- ^ The effect of the Indian Ocean trading system on the rise of Aksum is described in State Formation in Ancient Northeast Africa and the Indian Ocean Trade Archived 2009-01-14 at the Wayback Machine, by Stanley M. Burstein.
- ^ Crawford Young, The Rising Tide of Cultural Pluralism: The Nation-state at Bay?, (University of Wisconsin Press: 1993), p. 160
- ^ Rainer Baudendistel, Between Bombs and Good Intentions: The Red Cross and the Italo-Ethiopian War, (Berghahn Books: 2006), p. 320
- ^ George Kurian, Dictionary of world politics, (CQ Press: 2002), p. 150
- ^ Phillipson, David (2012). Foundations of an African Civilisation: Aksum and the northern Horn, 1000 BC – AD 1300. James Currey. p. 91. ISBN 978-1847010414.
- ^ G. Mokhtar, ed. (1990). UNESCO General History of Africa: Ancient Africa v. 2. University of California Press. p. 221. ISBN 978-0520066977.
- ^ Kaplan, Steve (1994). The Beta Israel (Falasha) in Ethiopia: From the Earliest Times to the Twentieth Century. New York University Press. ISBN 978-0814746646.
- ^ Munro-Hay, Stuart (2010). Henry Louis Gates Jr., Kwame Anthony Appiah (ed.). Encyclopedia of Africa Vol. I. Oxford University press. p. 77. ISBN 978-0195337709.
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-01-07. Retrieved 2017-01-06.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ Wybrew, Hugh. "A History of Christianity in the Middle East & North Africa". Jerusalem & Middle East Church Association. Retrieved 25 February 2013.
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-01-07. Retrieved 2017-01-06.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ Murray, S. The Library: An Illustrated History. New York, NY: Skyhorse Pub, 2009. Chicago : ALA Editions, 2009
Further reading[edit]
- Bausi, Alessandro (2018). "Translations in Late Antique Ethiopia" (PDF). Egitto Crocevia di Traduzioni. EUT Edizioni Università di Trieste. 1: 69–100. ISBN 978-88-8303-937-9.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Phillipson, David W. (1998). Ancient Ethiopia. Aksum: Its Antecedents and Successors. The British Museum Press. ISBN 978-0-7141-2763-7.
- Yule (ed.), Paul A. (2013). Late Antique Arabia Ẓafār, Capital of Ḥimyar, Rehabilitation of a 'Decadent' Society, Excavations of the Ruprecht-Karls-Universität Heidelberg 1998–2010 in the Highlands of the Yemen. Abhandlungen Deutsche Orient-Gesellschaft, vol. 29, Wiesbaden, pp. 251–54. ISBN 978-3-447-06935-9.CS1 maint: extra text: authors list (link)
External links[edit]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Kingdom of Aksum. |
- Ancient History Encyclopedia – Kingdom of Axum
- East-West Orientation of Historical Empires and Modern States at the Wayback Machine (archived February 22, 2007)
- Ethiopian Treasures – Queen of Sheba, Aksumite Kingdom – Aksum
- Ancient History Sourcebook: Accounts of Meröe, Kush, and Axum
- Aksum: UNESCO World Heritage Site
- The Ash Heap of History (Mises.org)





















