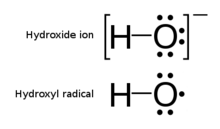
Hydroxyl radical
This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2010) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Hydroxyl radical
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name | |
| Other names
Hydroxy
Hydroxyl | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| 105 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| HO | |
| Molar mass | 17.007 g·mol−1 |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std molar
entropy (S |
183.71 J K−1 mol−1 |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
38.99 kJ mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
The hydroxyl radical, •OH, is the neutral form of the hydroxide ion (OH−). Hydroxyl radicals are highly reactive (easily becoming hydroxy groups) and consequently short-lived; however, they form an important part of radical chemistry.[2] Most notably hydroxyl radicals are produced from the decomposition of hydroperoxides (ROOH) or, in atmospheric chemistry, by the reaction of excited atomic oxygen with water. It is also an important radical formed in radiation chemistry, since it leads to the formation of hydrogen peroxide and oxygen, which can enhance corrosion and SCC in coolant systems subjected to radioactive environments. Hydroxyl radicals are also produced during UV-light dissociation of H2O2 (suggested in 1879) and likely in Fenton chemistry, where trace amounts of reduced transition metals catalyze peroxide-mediated oxidations of organic compounds.
In organic synthesis, hydroxyl radicals are most commonly generated by photolysis of 1-hydroxy-2(1H)-pyridinethione.
The hydroxyl radical is often referred to as the "detergent" of the troposphere because it reacts with many pollutants, decomposing them through "cracking", often acting as the first step to their removal. It also has an important role in eliminating some greenhouse gases like methane and ozone.[3] The rate of reaction with the hydroxyl radical often determines how long many pollutants last in the atmosphere, if they do not undergo photolysis or are rained out. For instance methane, which reacts relatively slowly with hydroxyl radical, has an average lifetime of >5 years and many CFCs have lifetimes of 50 years or more. Other pollutants, such as larger hydrocarbons, can have very short average lifetimes of less than a few hours.
The first reaction with many volatile organic compounds (VOCs) is the removal of a hydrogen atom, forming water and an alkyl radical (R•).
- •OH + RH → H2O + R•
The alkyl radical will typically react rapidly with oxygen forming a peroxy radical.
- R• + O2 → RO•
2
The fate of this radical in the troposphere is dependent on factors such as the amount of sunlight, pollution in the atmosphere and the nature of the alkyl radical that formed it.[4]
Notation[edit]
The unpaired electron of the hydroxyl radical is officially represented by a middle dot, ·, beside the O (or "\cdot" in LaTeX). [5]
Biological significance[edit]
Hydroxyl radicals can occasionally be produced as a byproduct of immune action. Macrophages and microglia most frequently generate this compound when exposed to very specific pathogens, such as certain bacteria. The destructive action of hydroxyl radicals has been implicated in several neurological autoimmune diseases such as HAND when immune cells become over-activated and toxic to neighboring healthy cells.[6]
The hydroxyl radical can damage virtually all types of macromolecules: carbohydrates, nucleic acids (mutations), lipids (lipid peroxidation), and amino acids (e.g. conversion of Phe to m-Tyrosine and o-Tyrosine).[7] The hydroxyl radical has a very short in vivo half-life of approximately 10−9 seconds and a high reactivity.[8] This makes it a very dangerous compound to the organism.[9][10]
Unlike superoxide, which can be detoxified by superoxide dismutase, the hydroxyl radical cannot be eliminated by an enzymatic reaction.[9]
Application in water purification[edit]
Hydroxyl radicals play a key role in the oxidative destruction of organic pollutant using a series of methodologies collectively known as advanced oxidation processes (AOPs). The destruction of pollutants in AOPs is based on the non-selective reaction of hydroxyl radicals on organic compounds. It is highly effective against a series of pollutants including pesticides, pharmaceutical compounds, dyes, etc.[11][12]
Importance in Earth's atmosphere[edit]
The hydroxyl •OH radical is one of the main chemical species controlling the oxidizing capacity of the global Earth atmosphere. This oxidizing reactive species has a major impact on the concentrations and distribution of greenhouse gases and pollutants in the Earth atmosphere. It is the most widespread oxidizer in the troposphere, the lowest part of the atmosphere. Understanding •OH variability is important to evaluating human impacts on the atmosphere and climate. The •OH species has a lifetime in the Earth atmosphere of less than one second.[13] Understanding the role of •OH in the oxidation process of methane (CH4) present in the atmosphere to first carbon monoxide (CO) and then carbon dioxide (CO2) is important for assessing the residence time of this greenhouse gas, the overall carbon budget of the troposphere, and its influence on the process of global warming. The lifetime of •OH radicals in the Earth atmosphere is very short, therefore •OH concentrations in the air are very low and very sensitive techniques are required for its direct detection.[14] Global average hydroxyl radical concentrations have been measured indirectly by analyzing methyl chloroform (CH3CCl3) present in the air. The results obtained by Montzka et al. (2011)[15] shows that the interannual variability in •OH estimated from CH3CCl3 measurements is small, indicating that global •OH is generally well buffered against perturbations. This small variability is consistent with measurements of methane and other trace gases primarily oxidized by •OH, as well as global photochemical model calculations.
In 2014, researchers reported their discovery of a "hole" or absence of hydroxyl throughout the entire depth of the troposphere across a large region of the tropical West Pacific. They suggested that this hole is permitting large quantities of ozone-degrading chemicals to reach the stratosphere, and that this may be significantly reinforcing ozone depletion in the polar regions with potential consequences for the climate of the Earth.[16]
Astronomical importance[edit]
First detection of interstellar •OH[edit]
The first experimental evidence for the presence of 18 cm absorption lines of the hydroxyl (•OH) radical in the radio absorption spectrum of Cassiopeia A was obtained by Weinreb et al. (Nature, Vol. 200, pp. 829, 1963) based on observations made during the period October 15–29, 1963.[17]
Important subsequent reports of astronomical •OH detections[edit]
| Year | Description |
|---|---|
| 1967 | •HO Molecules in the Interstellar Medium. Robinson and McGee. One of the first observational reviews of •OH observations. •OH had been observed in absorption and emission, but at this time the processes which populate the energy levels are not yet known with certainty, so the article does not give good estimates of •OH densities.[18] |
| 1967 | Normal •HO Emission and Interstellar Dust Clouds. Heiles. First detection of normal emission from •OH in interstellar dust clouds.[19] |
| 1971 | Interstellar molecules and dense clouds. D. M. Rank, C. H. Townes, and W. J. Welch. Review of the epoch about molecular line emission of molecules through dense clouds.[20] |
| 1980 | •HO observations of molecular complexes in Orion and Taurus. Baud and Wouterloot. Map of •OH emission in molecular complexes Orion and Taurus. Derived column densities are in good agreement with previous CO results.[21] |
| 1981 | Emission-absorption observations of HO in diffuse interstellar clouds. Dickey, Crovisier and Kazès. Observations of fifty eight regions which show HI absorption were studied. Typical densities and excitation temperature for diffuse clouds are determined in this article.[22] |
| 1981 | Magnetic fields in molecular clouds — •HO Zeeman observations. Crutcher, Troland, and Heiles. •OH Zeeman observations of the absorption lines produced in interstellar dust clouds toward 3C 133, 3C 123, and W51.[23] |
| 1981 | Detection of interstellar HO in the Far-Infrared. J. Storey, D. Watson, C. Townes. Strong absorption lines of •OH were detected at wavelengths of 119.23 and 119.44 microns in the direction of Sgr B2.[24] |
| 1989 | Molecular outflows in powerful HO megamasers. Baan, Haschick, and Henkel. Observations of •H and •OH molecular emission through •OH megamasers galaxies, in order to get a FIR luminosity and maser activity relation.[25] |
Energy levels[edit]
•OH is a diatomic molecule. The electronic angular momentum along the molecular axis is +1 or −1, and the electronic spin angular momentum S = 1⁄2. Because of the orbit-spin coupling, the spin angular momentum can be oriented in parallel or anti parallel directions to the orbital angular momentum, producing the splitting into Π1⁄2 and Π3⁄2 states. The 2Π3⁄2 ground state of •OH is split by lambda doubling interaction (an interaction between the nuclei rotation and the unpaired electron motion around its orbit). Hyperfine interaction with the unpaired spin of the proton further splits the levels.
Chemistry of the molecule •OH[edit]
In order to study gas phase interstellar chemistry, it is convenient to distinguish two types of interstellar clouds: diffuse clouds, with T = 30–100 K and n = 10–1000 cm−3, and dense clouds, with T = 10–30 K and density n = 104–103 cm−3. Ion chemical routes in both dense and diffuse clouds have been established for some works (Hartquist, Molecular Astrophysics, 1990).
•OH production pathways[edit]
The •OH radical is linked with the production of H2O in molecular clouds. Studies of •OH distribution in Taurus Molecular Cloud-1 (TMC-1)[26] suggest that in dense gas, •OH is mainly formed by dissociative recombination of H3O+. Dissociative recombination is the reaction in which a molecular ion recombines with an electron and dissociates into neutral fragments. Important formation mechanisms for •OH are:
-
H3O+ + e− → •OH + H2
(Dissociative recombination: 1a)
-
H3O+ + e− → •OH + •H + •H
(Dissociative recombination: 1b)
-
HCO+
2 + e− → •OH + CO(Dissociative recombination: 2a)
-
•O + HCO → •OH + CO
(Neutral–neutral: 3a)
-
H− + H3O+ → •OH + H2 + •H
(Ion–molecular ion neutralization: 4a)
•OH destruction pathways[edit]
Experimental data on association reactions of •H and •OH suggest that radiative association involving atomic and diatomic neutral radicals may be considered as an effective mechanism for the production of small neutral molecules in the interstellar clouds.[27] The formation of O2 occurs in the gas phase via the neutral exchange reaction between O and •OH, which is also the main sink for •OH in dense regions.[26]
We can see that atomic oxygen takes part both in the production and destruction of •OH, so the abundance of •OH depends mainly on the H3+ abundance. Then, important chemical pathways leading from •OH radicals are:
-
•OH + O → O2 + •H
(Neutral–neutral: 1A)
-
•OH + C+ → CO+ + •H
(Ion–neutral 2A)
-
•OH + •N → NO + •H
(Neutral–neutral: 3A)
-
•OH + C → CO + •H
(Neutral–neutral: 4A)
-
•OH + •H → H2O + photon
(Neutral–neutral: 5A)
Rate constants and relative rates for important formation and destruction mechanisms[edit]
Rate constants can be derived from the dataset published in a website.[28] Rate constants have the form:
- k(T) = α(T/300)β × exp(−γ/T) cm3 s−1
The following table has the rate constants calculated for a typical temperature in a dense cloud T = 10 K.
| Reaction | k (T = 10 K) cm3 s−1 |
|---|---|
| 1a | 3.29 × 10−6 |
| 1b | 1.41 × 10−7 |
| 2a | 4.71 × 10−7 |
| 3a | 5.0 × 10−11 |
| 4a | 1.26 × 10−6 |
| 5a | 2.82 × 10−6 |
| 1A | 7.7 × 10−10 |
| 2A | 3.5 × 10−11 |
| 3A | 1.38 × 10−10 |
| 4A | 1.0 × 10−10 |
| 5A | 3.33 × 10−14 |
Formation rates rix can be obtained using the rate constants k(T) and the abundances of the reactants species C and D:
- rix = k(T)ix[C][D]
where [Y] represents the abundance of the species Y. In this approach, abundances were taken from The UMIST database for astrochemistry 2006, and the values are relatives to the H2 density. Following table shows the ratio rix/r1a in order to get a view of the most important reactions.
| r1a | r1b | r2a | r3a | r4a | r5a | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r1a | 1.0 | 0.043 | 0.013 | 0.035 | 3.6 × 10−5 | 0.679 |
The results suggest that (1a) reaction is the most prominent reaction in dense clouds. It is in concordance with Harju et al. 2000.
The next table shows the results by doing the same procedure for destruction reaction:
| r1A | r2A | r3A | r4A | r5A | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r1A | 1.0 | 6.14 × 10−3 | 0.152 | 3.6 × 10−5 | 4.29 × 10−3 |
Results shows that reaction 1A is the main sink for •OH in dense clouds.
Importance of interstellar •OH observations[edit]
Discoveries of the microwave spectra of a considerable number of molecules prove the existence of rather complex molecules in the interstellar clouds, and provides the possibility to study dense clouds, which are obscured by the dust they contain.[29] The •OH molecule has been observed in the interstellar medium since 1963 through its 18-cm transitions.[30] In the subsequent years •OH was observed by its rotational transitions at far infrared wavelengths, mainly in the Orion region. Because each rotational level of •OH is split in by lambda doubling, astronomers can observe a wide variety of energy states from the ground state.
•OH as a tracer of shock conditions[edit]
Very high densities are required to thermalize the rotational transitions of •OH,[31] so it is difficult to detect far-infrared emission lines from a quiescent molecular cloud. Even at H2 densities of 106 cm−3, dust must be optically thick at infrared wavelengths. But the passage of a shock wave through a molecular cloud is precisely the process which can bring the molecular gas out of equilibrium with the dust, making observations of far-infrared emission lines possible. A moderately fast shock may produce a transient raise in the •OH abundance relative to hydrogen. So, it is possible that far-infrared emission lines of •OH can be a good diagnostic of shock conditions.
In diffuse clouds[edit]
Diffuse clouds are of astronomical interest because they play a primary role in the evolution and thermodynamics of ISM. Observation of the abundant atomic hydrogen in 21 cm has shown good signal-to-noise ratio in both emission and absorption. Nevertheless, HI observations have a fundamental difficulty when they are directed at low mass regions of the hydrogen nucleus, as the center part of a diffuse cloud: the thermal width of the hydrogen lines are of the same order as the internal velocities of structures of interest, so cloud components of various temperatures and central velocities are indistinguishable in the spectrum. Molecular line observations in principle do not suffer from this problem. Unlike HI, molecules generally have excitation temperature Tex ≪ Tkin, so that emission is very weak even from abundant species. CO and •OH are the most easily studied candidate molecules. CO has transitions in a region of the spectrum (wavelength < 3 mm) where there are not strong background continuum sources, but •OH has the 18 cm emission, line convenient for absorption observations.[22] Observation studies provide the most sensitive means of detections of molecules with subthermal excitation, and can give the opacity of the spectral line, which is a central issue to model the molecular region.
Studies based in the kinematic comparison of •OH and HI absorption lines from diffuse clouds are useful in determining their physical conditions, specially because heavier elements provide higher velocity resolution.
•OH masers[edit]
•OH masers, a type of astrophysical maser, were the first masers to be discovered in space and have been observed in more environments than any other type of maser.
In the Milky Way, •OH masers are found in stellar masers (evolved stars), interstellar masers (regions of massive star formation), or in the interface between supernova remnants and molecular material. Interstellar •OH masers are often observed from molecular material surrounding ultracompact H II regions (UC H II). But there are masers associated with very young stars that have yet to create UC H II regions.[32] This class of •OH masers appears to form near the edges of very dense material, place where H2O masers form, and where total densities drop rapidly and UV radiation form young stars can dissociate the H2O molecules. So, observations of •OH masers in these regions, can be an important way to probe the distribution of the important H2O molecule in interstellar shocks at high spatial resolutions.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ a b "Hydroxyl (CHEBI:29191)". Chemical Entities of Biological Interest (ChEBI). UK: European Bioinformatics Institute.
- ^ Hayyan M., Hashim M.A., AlNashef I.M. (2016). "Superoxide Ion: Generation and Chemical Implications". Chem. Rev. 116 (5): 3029–3085. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00407. PMID 26875845.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ "Trends in the Hydroxyl Free Radical" (PDF) (IPCC AR4 WG1). IPCC.
The hydroxyl free radical (OH) is the major oxidizing chemical in the atmosphere, destroying about 3.7 Gt of trace gases, including CH4 and all HFCs and HCFCs, each year (Ehhalt, 1999).
Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ (See chapters 12 & 13 in External Links "University Lecture notes on Atmospheric chemistry)
- ^ McNaught, A. D.; Wilkinson, A. "radical (free radical)". IUPAC. Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book"). Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford. Retrieved 12 April 2020.
- ^ Kincaid-Colton, Carol; Wolfgang Streit (November 1995). "The Brain's Immune System". Scientific American.
- ^ Reiter RJ, Melchiorri D, Sewerynek E; et al. (January 1995). "A review of the evidence supporting melatonin's role as an antioxidant". J. Pineal Res. 18: 1–11. doi:10.1111/j.1600-079x.1995.tb00133.x. PMID 7776173.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ Sies, Helmut (March 1993). "Strategies of antioxidant defense". European Journal of Biochemistry. 215 (2): 213–219. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18025.x. PMID 7688300.
- ^ a b Reiter RJ, Melchiorri D, Sewerynek E, et al. (January 1995). "A review of the evidence supporting melatonin's role as an antioxidant". J. Pineal Res. 18 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1111/j.1600-079x.1995.tb00133.x. PMID 7776173.
- ^ Reiter RJ, Carneiro RC, Oh CS (August 1997). "Melatonin in relation to cellular antioxidative defense mechanisms". Horm. Metab. Res. 29 (8): 363–72. doi:10.1055/s-2007-979057. PMID 9288572.
- ^ Sunil Paul, M. M.; Aravind, Usha K.; Pramod, G.; Aravindakumar, C.T. (April 2013). "Oxidative degradation of fensulfothion by hydroxyl radical in aqueous medium". Chemosphere. 91 (3): 295–301. Bibcode:2013Chmsp..91..295S. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.11.033. PMID 23273737.
- ^ Sreekanth R, Prasanthkumar KP, Sunil Paul MM, Aravind UK, Aravindakumar CT (Nov 7, 2013). "Oxidation reactions of 1- and 2-naphthols: an experimental and theoretical study". The Journal of Physical Chemistry A. 117 (44): 11261–70. Bibcode:2013JPCA..11711261S. doi:10.1021/jp4081355. PMID 24093754.
- ^ Isaksen, I.S.A.; S.B. Dalsøren (2011). "Getting a better estimate of an atmospheric radical". Science. 331 (6013): 38–39. Bibcode:2011Sci...331...38I. doi:10.1126/science.1199773. PMID 21212344.
- ^ Heal MR, Heard DE, Pilling MJ, Whitaker BJ (1995). "On the development and validation of FAGE for local measurement of tropospheric OH and HO2" (PDF). Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences. 52 (19): 3428–3448. Bibcode:1995JAtS...52.3428H. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(1995)052<3428:OTDAVO>2.0.CO;2. ISSN 1520-0469.
- ^ Montzka, S.A.; M. Krol; E. Dlugokencky; B. Hall; P. Jöckel; J. Lelieveld (2011). "Small interannual variability of global atmospheric hydroxyl". Science. 331 (6013): 67–69. Bibcode:2011Sci...331...67M. doi:10.1126/science.1197640. PMID 21212353. Retrieved 2011-01-09.
- ^ ["Like a giant elevator to the stratosphere", News Release, Alfred Wegener Institute, April 3, 2014]
- ^ Dieter, N. H.; Ewen, H. I. (1964). "Radio Observations of the Interstellar OH Line at 1,667 Mc/s". Nature. 201 (4916): 279–281. Bibcode:1964Natur.201..279D. doi:10.1038/201279b0. ISSN 0028-0836.
- ^ Robinson, B J; McGee, R X (1967). "OH Molecules in the Interstellar Medium". Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics. 5 (1): 183–212. Bibcode:1967ARA&A...5..183R. doi:10.1146/annurev.aa.05.090167.001151. ISSN 0066-4146.
- ^ Heiles, Carl E. (1968). "Normal OH Emission and Interstellar Dust Clouds". The Astrophysical Journal. 151: 919. Bibcode:1968ApJ...151..919H. doi:10.1086/149493. ISSN 0004-637X.
- ^ Rank, D. M.; Townes, C. H.; Welch, W. J. (1971). "Interstellar Molecules and Dense Clouds". Science. 174 (4014): 1083–1101. Bibcode:1971Sci...174.1083R. doi:10.1126/science.174.4014.1083. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 17779392.
- ^ Baud, B.; Wouterloot, J. G. A. (1980), "OH observations of molecular complexes in Orion and Taurus", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 90: 297, Bibcode:1980A&A....90..297B
- ^ a b Dickey, J. M.; Crovisier, J.; Kazes, I. (May 1981). "Emission-absorption observations of •HO in diffuse interstellar clouds". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 98 (2): 271–285. Bibcode:1981A&A....98..271D.
- ^ Crutcher, R. M.; Troland, T. H.; Heiles, C. (1981). "Magnetic fields in molecular clouds - OH Zeeman observations". The Astrophysical Journal. 249: 134. Bibcode:1981ApJ...249..134C. doi:10.1086/159268. ISSN 0004-637X.
- ^ Storey, J. W. V.; Watson, D. M.; Townes, C. H. (1981). "Detection of interstellar OH in the far-infrared". The Astrophysical Journal. 244: L27. Bibcode:1981ApJ...244L..27S. doi:10.1086/183472. ISSN 0004-637X.
- ^ Baan, Willem A.; Haschick, Aubrey D.; Henkel, Christian (1989). "Molecular outflows in powerful OH megamasers". The Astrophysical Journal. 346: 680. Bibcode:1989ApJ...346..680B. doi:10.1086/168050. ISSN 0004-637X.
- ^ a b Harju, J.; Winnberg, A.; Wouterloot, J. G. A. (2000), "The distribution of OH in Taurus Molecular Cloud-1", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 353: 1065, Bibcode:2000A&A...353.1065H
- ^ Field, D.; Adams, N. G.; Smith, D. (1980), "Molecular synthesis in interstellar clouds - The radiative association reaction H + OH yields H2O + h/nu/", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 192: 1–10, Bibcode:1980MNRAS.192....1F, doi:10.1093/mnras/192.1.1
- ^ "The UMIST Database for Astrochemistry 2012 / astrochemistry.net".
- ^ Rank, D. M.; Townes, C. H.; Welch, W. J. (1971-12-01). "Interstellar Molecules and Dense Clouds". Science. 174 (4014): 1083–1101. Bibcode:1971Sci...174.1083R. doi:10.1126/science.174.4014.1083. PMID 17779392.
- ^ Dieter, N. H.; Ewen, H. I. (1964-01-18). "Radio Observations of the Interstellar HO Line at 1,667 Mc/s". Nature. 201 (4916): 279–281. Bibcode:1964Natur.201..279D. doi:10.1038/201279b0.
- ^ Storey, J. W. V.; Watson, D. M.; Townes, C. H. (1981-02-15). "Detection of interstellar HO in the far-infrared". Astrophysical Journal Letters. 244: L27–L30. Bibcode:1981ApJ...244L..27S. doi:10.1086/183472.
- ^ Argon, Alice L.; Reid, Mark J.; Menten, Karl M. (August 2003). "A class of interstellar •HO masers associated with protostellar outflows". The Astrophysical Journal. 593 (2): 925–930. arXiv:astro-ph/0304565. Bibcode:2003ApJ...593..925A. doi:10.1086/376592.
- Downes A.; Blunt T.P. (1879). "The effect of sunlight upon hydrogen peroxide". Nature. 20 (517): 521. Bibcode:1879Natur..20Q.521.. doi:10.1038/020521a0.