Lar gibbon
| Lar gibbon[1] | |
|---|---|

| |
| in Austria, at the Zoo Salzburg | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Primates |
| Suborder: | Haplorhini |
| Infraorder: | Simiiformes |
| Family: | Hylobatidae |
| Genus: | Hylobates |
| Species: | H. lar
|
| Binomial name | |
| Hylobates lar (Linnaeus, 1771)
| |
| |
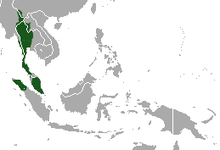
| Lar gibbon range | |
The lar gibbon (Hylobates lar), also known as the white-handed gibbon, is an endangered primate in the gibbon family, Hylobatidae. It is one of the better-known gibbons and is often kept in captivity.
Taxonomy[edit]
There are five subspecies of lar gibbon:[1][3]
- Malaysian lar gibbon (H. l. lar)
- Carpenter's lar gibbon (H. l. carpenteri)
- Central lar gibbon (H. l. entelloides)
- Sumatran lar gibbon (H. l. vestitus)
- Yunnan lar gibbon (H. l. yunnanensis (possibly extinct))
Physical description[edit]
The fur coloring of the lar gibbon varies from black and dark-brown to light-brown, sandy colors. The hands and feet are white-colored, likewise a ring of white hair surrounds the black face. Both males and females can be all color variants, and the sexes also hardly differ in size. Gibbons are true brachiators, propelling themselves through the forest by swinging under the branches using their arms. Reflecting this mode of locomotion, the white-handed gibbon has curved fingers, elongated hands, extremely long arms and relatively short legs, giving it an intermembral index of 129.7, one of the highest of the primates.[4] As with all apes, the number of caudal vertebrae has been reduced drastically, resulting in the loss of a functional tail. Gibbons have tough, bony padding on their buttocks, known as the ischial callosities, or sitting pads.
Distribution and habitat[edit]
Lar gibbons have the greatest north-south range of any of the gibbon species.[5] They are found in Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar and Thailand.[6] Their range historically extended from southwest China to Thailand and Burma south to the whole Malay Peninsula in primary and secondary tropical rain forests. It is also present in the northwest portion of the island of Sumatra. In recent decades, especially, the continental range has been reduced and fragmented. Lar gibbons are likely extinct in China, but if they still exist, they would only be found in southwest Yunnan, their former range.[7]
Lar gibbon are usually found in lowland dipterocarp forest, hill dipterocarp forest, and upper dipterocarp forest, including primary lowland and submontane rainforest, mixed deciduous bamboo forest, and seasonal evergreen forest. They are not usually found higher than 1200 meters above sea level.[8] The gibbon genus is highly allopatric, usually separated by large rivers. As a result, their range extends through southern and eastern Myanmar, but only east of the Salween River. They are found through the Malay Peninsula. Lar gibbons also exist west of the Mekong River in northwestern Laos and northern Sumatra.[9] The lar gibbon can be found living in sympatry with several other primates and apes, including orangutans (Pongo pygmaeus), siamangs (S. syndactylus), pileated gibbons (Hylobates pileatus), purple-faced langurs (Trachypithecus spp.), Thomas's langur (Presbytis thomasi), slow loris (Nycticebus coucang), and several macaques (Macaca spp.)[10] In Thailand, lar gibbons probably number between 15,000 and 20,000, though there may be as few as 10 in China, if any.[11]
Diet and dentition[edit]
The lar gibbon is considered frugivorous with fruit constituting 50% of its diet, but leaves (29%) are a substantial part, with insects (13%) and flowers (9%) forming the remainder.[4] In the wild, lar gibbons will eat a large variety of foods, including figs and other small, sweet fruits, liana fruit, tree fruit and berries, as well as young leaves, buds and flowers, new shoots, vines, vine shoots, and insects, including mantids and wasps, and even birds' eggs.[12] During the summer months, when figs and leaves are less available, insect consumption increases twenty-fold relative to the winter.[13]
Its dental formula is 2.1.2.32.1.2.3, the generalized formula for Old World monkeys and apes (including humans). The dental arcade is U-shaped, and the mandible is thin and light. The incisors are broad and flat, while the molars have low, rounded cusps with thick enamel. The most noticeable characteristic of the dentition of Hylobates lar is the presence of large, dagger-like canines in both the upper and lower jaw. These canines are not sexually dimorphic.
Behavior[edit]

Lar gibbons are diurnal and arboreal, inhabiting rain forests. Lar gibbons are usually active for an average of 8.7 hours per day, leaving their sleeping sites right around sunrise and entering sleeping trees an average of 3.4 hours before sunset. On average, lar gibbons spend their days feeding (32.6%), resting (26.2%), traveling (24.2%), in social activities (11.3%), vocalizing (4.0%) and in intergroup encounters (1.9%), although actual proportions of activities can change significantly over the course of the year.[13] They rarely come to the ground, instead using their long arms to brachiate through the trees. With their hooked hands, they can move swiftly with great momentum, swinging from the branches. Although they rarely come to the ground naturally, while there, they walk bipedally with arms raised above their heads for balance. Their social organization is dominated by monogamous family pairs, with one breeding male and one female along with their offspring. When a juvenile reaches sexual maturity, it is expelled from the family unit. However, this traditional conception has come under scrutiny. Long-term studies conducted in Khao Yai National Park in Thailand suggest their mating system is somewhat flexible, incorporating extra-pair copulations, partner changes and polyandrous groupings.[14] This multimale polandry may be attributed to cooperative territory use and female defense. As range size increases, males are more successful in defending it in a pair or group.[15] Additionally, these extra pair copulations may increase the chance of reproduction with a mate of superior genetic quality and decrease the chance of infanticide.[16]
Vocalisations[edit]
Family groups inhabit a firm territory, which they protect by warding off other gibbons with their calls. Each morning, the family gathers on the edge of its territory and begins a "great call", a duet between the breeding pair. Each species has a typified call and each breeding pair has unique variations on that theme. The great call of Hylobates lar is characterized by its frequent use of short hoots with more complex hoots, along with a "quavering" opening and closing.[17] These calls are one of the traits used determining species differences among the gibbons.[3] Recent studies indicate that gibbon song have evolved to communicate conflict in terms of predation. In the presence of Asiatic tiger, clouded leopard, crested serpent eagle and reticulated python songs were more likely to contain sharp wow elements than normal duets.[18]
Reproduction[edit]
Sexually, they are similar to other gibbons. Mating occurs in every month of the year, but most conceptions occur during the dry season in March, with a peak in births during the late rainy season, in October.[19] On average, females reproduce for the first time at about 11 years of age in the wild, much later than in captivity.[20] Gestation is six months long on average, and pregnancies are usually of a single young. Young are nursed for approximately two years, and full maturity comes at about eight years. The life expectancy of the lar gibbons in the wild is about 25 years.[21]
Conservation[edit]
Lar gibbons are threatened in various ways: they are sometimes hunted for their meat, sometimes a parent is killed to capture young animals for pets, but perhaps the most pervasive is the loss of habitat. Lar gibbon habitats are already threatened by forest clearance for the construction of roads, agriculture, ecotourism, domesticated cattle and elephants, forest fires, subsistence logging, illegal logging, new village settlement, and palm oil plantations.[22]
References[edit]
- ^ a b Groves, C. P. (2005). "Order Primates". In Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 179–180. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- ^ Brockelman, W.; Geissmann, T. (2008). "Hylobates lar". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2008: e.T10548A3199623. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2008.RLTS.T10548A3199623.en.
- ^ a b Geissmann, Thomas. "Gibbon Systematics and Species Identification". Retrieved 2006-04-13.
- ^ a b Rowe, Noel. Pictorial Guide to the Living Primates. East Hampton, N.Y. : Pogonias Press, 1996.
- ^ Barlett, T.Q. (2003). Intragroup and intergroup social interactions in white-handed gibbons. Int J Primatol. pp. 239–59.
- ^ Brandon-Jones, D (2004). Asian primate classification. Int J Primatol. pp. 97–164.
- ^ Brandon-Jones D, Eudey AA, Geissmann T Groves CP, Melnick DJ, Morales JC, Shekelle M, Stewart (2004). Asian primate classification. Int J Primatol. pp. 97–164.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ Chivers DJ (1972). The siamang and the gibbon in the Malay Peninsula. Gibb Siam 1. pp. 103–35.
- ^ Brockelman WY, Reichard U, Treesucon U, Raemaekers JJ (1998). Dispersal, pair formation and social structure in gibbons (Hylobates lar). Behav Ecol Sociobiol 42. pp. 329–39.
- ^ Ellefson JO (1974). A natural history of white-handed gibbons in the Malayan peninsula. Gibb Siam 3. pp. 1–136.
- ^ Geissmann, T. (2007). "Status reassessment of the gibbons: results of the Asian primate red list workshop 2006". Gibbon Journal. 3: 5–15. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.694.8483.
- ^ Carpenter CR. (1940). A field study in Siam of the behavior and social relations of the gibbon (Hylobates lar). Comp Psychol Mono 16. pp. 1–212.
- ^ a b Bartlett TQ. (2009). The gibbons of Khao Yai: seasonal variation in behavior and ecology. Upper Saddle River. Pearson Prentice Hall. p. 170.
- ^ Sommer, V.; Reichard, U. (2000). "Rethinking Monogamy: The Gibbon Case". In P. Kappeler (ed.). Primate Males. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 159–168.
- ^ Reichard, Ulrich H. (2009). "The social organization and mating system of Khao Yai white-handed gibbons: 1992-2006.". The Gibbons. New York: Springer. pp. 347–384. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-88604-6_17. ISBN 978-0-387-88603-9.
- ^ Reichard, U.; Sommer, V. (1997). "Group Encounters in Wild Gibbons (Hylobates Lar): Agonism, Affiliation, and the Concept of Infanticide". Behaviour. 134 (15): 1135–1174. doi:10.1163/156853997x00106.
- ^ Geissmann, Thomas. "Sound Gallery: Hylobates lar". Retrieved 2009-04-29.
- ^ Clarke, E. (2011). "The Anti-Predator Behaviour of Wild White-Handed Gibbons (Hylobates Lar)" (PDF). Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology.
- ^ Barelli C, Heistermann M, Boesch C, Reichard UH (2008). Mating patterns and sexual swellings in pair-living and multimale groups of wild white-handed gibbons, Hylobates lar (PDF). Anim Behav 75(3). pp. 991–1001.
- ^ Barelli C, Boesch C, Heistermann M, Reichard UH (2008). Female white-handed gibbons (Hylobates lar) lead group movements and have priority of access to food resources (PDF). Behaviour 145. pp. 965–81.
- ^ Barelli C, Heistermann M, Boesch C, Reichard UH (2007). Sexual swellings in wild white-handed gibbon females (Hylobates lar) indicate the probability of ovulation. Horm Behav 51. pp. 221–30. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.516.8946.
- ^ Yimkao P, Srikosamatara S (2006). Ecology and site-based conservation of the white-handed gibbon (Hylobates lar L.) in human-use forests in Mae Hong Son province, northern Thailand. Nat Hist Bull Siam Soc 54. pp. 109–38.
External links[edit]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Lar gibbon. |
| Wikispecies has information related to Lar gibbon |
- ARKive - images and movies of the white-handed gibbon (Hylobates lar)
- Lar Gibbon photos
- Lar Gibbon songs
- Gibbon Conservation Center
- Lar Gibbon at Animal Diversity Web
- Thomas Geissmann's Gibbon Research Lab and Gibbon Network
- IUCN Red List endangered species
- Hylobates
- Primates of Southeast Asia
- Endangered fauna of Asia
- Species endangered by the pet trade
- Species endangered by use as food
- Species endangered by logging
- Species endangered by deforestation
- Species endangered by agriculture
- Species endangered by roadbuilding
- Species endangered by oil palm plantations
- Mammals described in 1771





