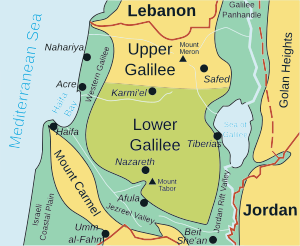
Galilee

Galilee (Hebrew: הַגָּלִיל, HaGalil; Arabic: الجليل, romanized: al-Jalīl) is a region mainly located in northern Israel. The term Galilee traditionally refers to the mountainous part, divided into Upper Galilee (Hebrew: גליל עליון, romanized: Galil Elyon) and Lower Galilee (Hebrew: גליל תחתון, romanized: Galil Tahton).
In modern, common usage, as well at different times in history, Galilee referred and refers to all of the area that is north of the Mount Carmel-Mount Gilboa ridge. In this sense, it extends from the Israeli coastal plain and the shores of the Mediterranean Sea with Acre in the west, to the Jordan Rift Valley to the east; and from the Lebanese border in the north plus a piece bordering on the Golan Heights all the way to Dan at the base of Mount Hermon in the northeast, to Mount Carmel and Mount Gilboa in the south. This definition includes the plains of the Jezreel Valley north of Jenin and the Beth Shean Valley, the valley containing the Sea of Galilee, and the Hula Valley, although it usually does not include Haifa's immediate northern suburbs. By this definition it overlaps with much of the administrative Northern District of the country (which also includes the Golan Heights and part of Menashe Heights, but not Qiryat Tiv'on).
Western Galilee (Hebrew: גליל מערבי, romanized: Galil Ma'aravi) is a common term referring to the western part of the Upper Galilee and its shore, and usually also the northwestern part of the Lower Galilee, mostly overlapping with Acre sub-district. Galilee Panhandle is a common term referring to the "panhandle" in the east that extends to the north, where Lebanon is to the west, and includes Hula Valley and Ramot Naftali mountains of the Upper Galilee.
Historically, the part of Southern Lebanon south of the east-west section of the Litani River also belonged to the region of Galilee, but the present article mainly deals with the Israeli part of the region.
Etymology
The region's Israelite name is from the Hebrew root גָּלִיל (galíl), an ultimately unique word for 'district', and usually 'cylinder'. The Hebrew form used in Isaiah 8:23 (or 9:1 in different Biblical versions) is in the construct state, g'lil ha-goyím (Hebrew: גְּלִיל הַגּוֹיִם), meaning 'Galilee of the nations', i.e. the part of Galilee inhabited by Gentiles at the time that the book was written.
The region in turn gave rise to the English name for the "Sea of Galilee" referred to as such in many languages including ancient Arabic. In the Hebrew language, the lake is referred to as Kinneret (Numbers 34:11, etc.), from Hebrew kinnor ('harp', describing its shape); Lake of Gennesaret (Luke 5:1, etc.), from Ginosar, from ge ('valley') and either netser ('branch') or natsor ('to guard', 'to watch'), which may have been a reference to Nazareth town;[citation needed] and alternatively named the Sea of Tiberias (John 6:1, etc.), from the town of Tiberias at its southwestern end, itself named after the first-century CE Roman emperor Tiberius. These are the three names used in originally internal Jewish-authored literature rather than the "Sea of Galilee".[1] However, Jews did use "the Galilee" to refer to the whole region (Aramaic הגלילי), including its lake.
Geography
Most of Galilee consists of rocky terrain, at heights of between 500 and 700 m. Several high mountains are in the region, including Mount Tabor and Mount Meron, which have relatively low temperatures and high rainfall. As a result of this climate, flora and fauna thrive in the region, while many birds annually migrate from colder climates to Africa and back through the Hula–Jordan corridor. The streams and waterfalls, the latter mainly in Upper Galilee, along with vast fields of greenery and colourful wildflowers, as well as numerous towns of biblical importance, make the region a popular tourist destination.
Due to its high rainfall 900 millimetres (35 in)–1,200 millimetres (47 in), mild temperatures and high mountains (Mount Meron's elevation is 1,000–1,208 m), the upper Galilee region contains some distinctive flora and fauna: prickly juniper (Juniperus oxycedrus), Lebanese cedar (Cedrus libani), which grows in a small grove on Mount Meron, cyclamens, paeonias, and Rhododendron ponticum which sometimes appears on Meron.
History
Iron Age and Hebrew Bible
According to the Bible, Galilee was named by the Israelites and was the tribal region of Naphthali and Dan, at times overlapping the Tribe of Asher's land.[2] However, Dan was dispersed among the whole people rather than isolated to the lands of Dan, as the Tribe of Dan was the hereditary local law enforcement and judiciary for the whole nation.[3][non-primary source needed] Normally,[when?] Galilee is just referred to as Naphthali.
Chapter 9 of 1 Kings states that Solomon rewarded his Phoenician ally, King Hiram I of Sidon, with twenty cities in the land of Galilee, which would then have been either settled by foreigners during and after the reign of Hiram, or by those who had been forcibly deported there by later conquerors such as the Assyrians. Hiram, to reciprocate previous gifts given to David, accepted the upland plain among the mountains of Naphtali and renamed it "the land of Cabul" for a time.[4]
Classical antiquity

During the expansion under the Hasmonean dynasty much of the Galilee region was conquered and annexed by the first Hasmonean King of Judaea Aristobulus I (104 - 103 BCE). Galilee in the first century was dotted with small towns and villages.[6] The Jewish historian Josephus claims that there were 204 small towns in Galilee,[6] but modern scholars believe this estimate to be an exaggeration.[6] Many of these towns were located around the Sea of Galilee, which contained many edible fish and which was surrounded by fertile land.[6] Salted, dried, and pickled fish were an important export good.[6] In 4 BCE, a rebel named Judah plundered Galilee's largest city, Sepphoris. In response, the Syrian governor Publius Quinctilius Varus sacked Sepphoris and sold the population into slavery.[6]
After the death of Herod the Great that same year, the Roman emperor Augustus appointed his son Herod Antipas as tetrarch of Galilee, which remained a Roman client state.[5] Antipas paid tribute to the Roman Empire in exchange for Roman protection.[5] The Romans did not station troops in Galilee, but threatened to retaliate against anyone who attacked it.[5] As long as he continued to pay tribute, Antipas was permitted to govern however he wished[5] and was permitted to mint his own coinage.[5] Antipas was relatively observant of Jewish laws and customs.[5] Although his palace was decorated with animal carvings, which many Jews regarded as a transgression against the law prohibiting idols,[5] his coins bore only agricultural designs, which his subjects deemed acceptable.[5]

In general, Antipas was a capable ruler;[5] Josephus does not record any instance of him using force to put down an uprising and he had a long, prosperous reign.[5] However, many Jews probably resented him as not sufficiently devout.[5] Antipas rebuilt the city of Sepphoris[6] and, in either 18 CE or 19 CE, he founded the new city of Tiberias.[5] These two cities became Galilee's largest cultural centers.[5] They were the main centers of Greco-Roman influence, but were still predominantly Jewish.[6] A massive gap existed between the rich and poor,[6] but lack of uprisings suggest that taxes were not exorbitantly high and that most Galileans did not feel their livelihoods were being threatened.[5]
The archaeological discoveries of synagogues from the Hellenistic and Roman period in the Galilee show strong Phoenician influences, and a high level of tolerance for other cultures relative to other Jewish religious centers.[7] Late in his reign, Antipas married his half-niece Herodias, who was already married to one of her other uncles.[5] His wife, whom he divorced, fled to her father Aretas, an Arab king, who invaded Galilee and defeated Antipas's troops before withdrawing.[5] Both Josephus and the Gospel of Mark 6:17–29 record that the itinerate preacher John the Baptist criticized Antipas over his marriage[5] and Antipas consequently had him imprisoned and then beheaded.[5]
In around 39 CE, at the urging of Herodias, Antipas went to Rome to request that he be elevated from the status of tetrarch to the status of king.[5] The Romans found him guilty of storing arms, so he was removed from power and exiled, ending his forty-three-year reign.[5] During the Great Revolt (66–73 CE), a Jewish mob destroyed Herod Antipas's palace.[5] According to medieval Hebrew legend, Simeon bar Yochai, one of the most famed of all the Tannaim, wrote the Zohar while living in Galilee.[8] Eastern Galilee retained a Jewish majority until at least the seventh century.[9]
Early Muslim and Crusader periods
After the Muslim Arab caliphate took control of the region in 638, it became part of Jund al-Urdunn (District of Jordan). Its major towns were Tiberias (which was capital of the district—Qadas), Baysan, Acre, Saffuriya, and Kabul.[10]
The Shia Fatimids conquered the region in the 10th century; a breakaway sect, venerating the Fatimid caliph al-Hakim, formed the Druze religion, centered in Mount Lebanon and partially in the Galilee. During the Crusades, Galilee was organized into the Principality of Galilee, one of the most important Crusader seigneuries.
Ottoman era
During Early Ottoman era, the Galilee was governed as the Safad Sanjak, initially part of the larger administrative unit of Damascus Eyalet (1549–1660) and later as part of Sidon Eyalet (1660–1864). During the 18th century, the administrative division of Galilee was renamed to Acre Sanjak, and the Eyalet itself became centered in Acre, factually becoming the Acre Eyalet between 1775 and 1841.
The Jewish population of Galilee increased significantly following their expulsion from Spain and welcome from the Ottoman Empire. The community for a time made Safed an international center of cloth weaving and manufacturing, as well as a key site for Jewish learning.[11] Today it remains one of Judaism's four holy cities and a center for kabbalah.
In the mid-17th century Galilee and Mount Lebanon became the scene of the Druze power struggle, which came in parallel with much destruction in the region and decline of major cities.
In the mid-18th century, Galilee was caught up in a struggle between the Arab leader Zahir al-Umar and the Ottoman authorities who were centred in Damascus. Zahir ruled Galilee for 25 years until Ottoman loyalist Jezzar Pasha conquered the region in 1775.
In 1831, the Galilee, a part of Ottoman Syria, switched hands from Ottomans to Ibrahim Pasha of Egypt until 1840. During this period, aggressive social and politic policies were introduced, which led to a violent 1834 Arab revolt. In the process of this revolt the Jewish community of Safed was greatly reduced, in the event of Safed Plunder by the rebels. The Arab rebels were subsequently defeated by the Egyptian troops, though in 1838, the Druze of Galilee led another uprising. In 1834 and 1837, major earthquakes leveled most of the towns, resulting in great loss of life.
Following the 1864 Tanszimat reforms in the Ottoman Empire, the Galilee remained within Acre Sanjak, but was transferred from Sidon Eyalet to the newly formed Syria Vilayet and shortly, from 1888, became administered from Beirut Vilayet.
In 1866, Galilee's first hospital, the Nazareth Hospital, was founded under the leadership of American-Armenian missionary Dr. Kaloost Vartan, assisted by German missionary John Zeller.

In the early 20th century, Galilee remained part of Acre Sanjak of Ottoman Syria. It was administered as the southernmost territory of the Beirut Vilayet.
British administration
Following the defeat of the Ottoman Empire in World War I, and the Armistice of Mudros, it came under British rule, as part of the Occupied Enemy Territory Administration. Shortly after, in 1920, the region was included in the British Mandate territory, officially a part of Mandatory Palestine from 1923.
Israeli period
After the 1948 Arab–Israeli war, nearly the whole of Galilee came under Israel's control. A large portion of the population fled or was forced to leave, leaving dozens of entire villages empty; however, a large Israeli Arab community remained based in and near the cities of Nazareth, Acre, Tamra, Sakhnin, and Shefa-'Amr, due to some extent to a successful rapprochement with the Druze. The kibbutzim around the Sea of Galilee were sometimes shelled by the Syrian army's artillery until Israel seized Western Golan Heights in the 1967 Six-Day War.
During the 1970s and the early 1980s, the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) launched multiple attacks on towns and villages of the Upper and Western Galilee from Lebanon. This came in parallel to the general destabilization of Southern Lebanon, which became a scene of fierce sectarian fighting which deteriorated into the Lebanese Civil War. On the course of the war, Israel initiated Operation Litani (1979) and Operation Peace For Galilee (1982) with the stated objectives of destroying the PLO infrastructure in Lebanon, protecting the citizens of the Galilee and supporting allied Christian Lebanese militias. Israel took over much of southern Lebanon in support of Christian Lebanese militias until 1985, when it withdrew to a narrow security buffer zone.
From 1985 to 2000, Hezbollah, and earlier Amal, engaged the South Lebanon Army supported by the Israel Defense Forces, sometimes shelling Upper Galilee communities with Katyusha rockets. In May 2000, Israeli prime minister Ehud Barak unilaterally withdrew IDF troops from southern Lebanon, maintaining a security force on the Israeli side of the international border recognized by the United Nations. The move brought a collapse to the South Lebanon Army and takeover of Southern Lebanon by Hezbollah. However, despite Israeli withdrawal, clashes between Hezbollah and Israel continued along the border, and UN observers condemned both for their attacks.
The 2006 Israel-Lebanon conflict was characterized by round-the-clock Katyusha rocket attacks (with a greatly extended range) by Hezbollah on the whole of Galilee, with long-range, ground-launched missiles hitting as far south as the Sharon Plain, Jezreel Valley, and Jordan Valley below the Sea of Galilee.
Demography
As of 2006[update], there were 1.2 million residents in Galilee, of which 47% were Jewish.[12] The Jewish Agency has attempted to increase the Jewish population in this area,[13] but the non-Jewish population also has a high growth rate.[12]
The largest cities in the region are Acre, Nahariya, Nazareth, Safed, Karmiel, Shaghur, Shefa-'Amr, Afula, and Tiberias.[14] The port city of Haifa serves as a commercial center for the whole region.
Because of its hilly terrain, most of the people in the Galilee live in small villages connected by relatively few roads.[15] A railroad runs south from Nahariya along the Mediterranean coast, and a fork to the east is due to operate in 2015. The main sources of livelihood throughout the area are agriculture and tourism. Industrial parks are being developed, bringing further employment opportunities to the local population which includes many recent immigrants. The Israeli government is contributing funding to the private initiative, the Galilee Finance Facility, organised by the Milken Institute and Koret Economic Development Fund.[16]
The Galilee is home to a large Arab population,[17][18] comprising a Muslim majority and two smaller populations, of Druze and Arab Christians, of comparable sizes. Both Israeli Druze and Christians have their majorities in the Galilee.[19][20] Other notable minorities are the Bedouin, the Maronites and the Circassians.
The north-central portion of the Galilee is also known as Central Galilee, stretching from the border with Lebanon to the northern edge of the Jezreel Valley, including the cities of Nazareth and Sakhnin, has an Arab majority of 75% with most of the Jewish population living in hilltop cities like Upper Nazareth. The northern half of the central Lower Galilee, surrounding Karmiel and Sakhnin is known as the "Heart of the Galilee". The eastern Galilee is nearly 100% Jewish. This part includes the Finger of the Galilee, the Jordan River Valley, and the shores the Sea of Galilee, and contains two of Judaism's Four Holy Cities. The southern part of the Galilee, including Jezreel Valley, and the Gilboa region are also nearly 100% Jewish, with a few small Arab villages near the West Bank border. About 80% of the population of the Western Galilee is Jewish, all the way up to the Lebanese border. Jews also form a small majority in the mountainous Upper Galilee with a significant minority Arab population (mainly Druze and Christians).
As of 2011, the Galilee is attracting significant internal migration of Haredi Jews, who are increasingly moving to the Galilee and Negev as an answer to rising housing prices in central Israel.[21]
Tourism
Galilee is a popular destination for domestic and foreign tourists who enjoy its scenic, recreational, and gastronomic offerings. The Galilee attracts many Christian pilgrims, as many of the miracles of Jesus occurred, according to the New Testament, on the shores of the Sea of Galilee—including his walking on water, calming the storm, and feeding five thousand people in Tabgha. In addition, numerous sites of biblical importance are located in the Galilee, such as Megiddo, Jezreel Valley, Mount Tabor, Hazor, Horns of Hattin, and more.
A popular hiking trail known as the yam leyam, or sea-to-sea, starts hikers at the Mediterranean. They then hike through the Galilee mountains, Tabor, Neria, and Meron, until their final destination, the Kinneret (Sea of Galilee).
In April 2011, Israel unveiled the "Jesus Trail", a 40-mile (60-km) hiking trail in the Galilee for Christian pilgrims. The trail includes a network of footpaths, roads, and bicycle paths linking sites central to the lives of Jesus and his disciples, including Tabgha, the traditional site of Jesus' miracle of the loaves and fishes, and the Mount of Beatitudes, where he delivered his Sermon on the Mount. It ends at Capernaum on the shores of the Sea of Galilee, where Jesus espoused his teachings.[22]
Many kibbutzim and moshav families operate Zimmern (German: "rooms", the local term for a Bed and breakfasts). Numerous festivals are held throughout the year, especially in the autumn and spring holiday seasons. These include the Acre (Acco) Festival of Alternative Theater,[23] the olive harvest festival, music festivals featuring Anglo-American folk, klezmer, Renaissance, and chamber music, and Karmiel Dance Festival.
Cuisine
The cuisine of the Galilee is very diverse. The meals are lighter than in the central and southern regions. Dairy products are heavily consumed (especially the Safed cheese that originated in the mountains of the Upper Galilee). Herbs like thyme, mint, parsley, basil, and rosemary are very common with everything including dips, meat, fish, stews and cheese. In the eastern part of the Galilee, there is freshwater fish as much as meat (especially the Tilapia that lives in the Sea of Galilee, Jordan river, and other streams in the region), including fish filled with thyme and grilled with rosemary to flavor, or stuffed with oregano leaves, then topped with parsley and served with lemon to squash. This technique exists in other parts of the country including the coasts of the Mediterranean and the Red Sea. A specialty of the region is a baked Tilapia flavored with celery, mint and a lot of lemon juice. Baked fish with tahini is also common in Tiberias while the coastal Galileans prefer to replace the tahini with yogurt and add sumac on top.
The Galilee is famous for its olives, pomegranates, wine and especially its Labneh w'Za'atar which is served with pita bread, meat stews with wine, pomegranates and herbs such as akub, parsley, khalmit, mint, fennel, etc. are common. Galilean kubba is usually flavored with cumin, cinnamon, cardamom, concentrated pomegranate juice, onion, parsley and pine nuts and served as meze with tahini dip. Kebabs are also made almost in the same way with sumac replacing cardamom and with carob sometimes replacing the pomegranate juice. Because of its climate, beef has become more popular than lamb, although both are still eaten there. Dates are popular in the tropical climate of the Eastern Galilee.
Subregions
The Galilee is often divided into these subregions, which often overlap:
- Lower Galilee covers the area north of the Valleys (Jezreel, Harod and Beth Shean Valley) and south of the Beit HaKerem Valley. Its borders to the east on the Jordan Rift Valley. It contains the Arab city of Nazareth and the village of Cana.
- Upper Galilee extends from the Beit HaKerem Valley northwards into southern Lebanon. Its eastern border is the Hula Valley and the Sea of Galilee separating it from the Golan Heights. To the west it reaches to the Coastal Plain which separates it from the Mediterranean.
- The Jezreel Valley
- The "Galilee Panhandle" (Hebrew: אצבע הגליל, Etzba HaGalil, lit. "Finger of Galilee") is a panhandle along the Hulah Valley; it contains the towns of Metulla and Qiryat Shemona, and the Dan and part of the Banias rivers.
- The Jordan Valley from the southern tip of the Sea of Galilee down to Beit She'an.
- The Hula Valley
- The Korazim Plateau
- The Sea of Galilee and its valley
- The Beit She'an valley at the junction of the Jordan and extended Jezreel Valleys
- Mount Gilboa
- Western Galilee in its minimal definition refers to the coastal plain just west of the Upper Galilee, also known as Plain of Asher, or Plain of the Galilee, which stretches from north of Acre at Rosh HaNikra on the Israel-Lebanon border, and in the common broad definition adds the western part of Upper Galilee, and usually the northwestern part of Lower Galilee as well, corresponding more or less to Acre sub-district or the Northern District.
Gallery

See also
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Galilee. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Galilee. |
External links
- Galilee (definition of) on Haaretz.com
References
- ^ Room, Adrian (2006). Placenames of the World: Origins and Meanings of the Names for 6,600 Countries, Cities, Territories, Natural Features, and Historic Sites (2nd ed.). McFarland. p. 138. ISBN 978-0-7864-2248-7.
- ^ "Map of the Twelve Tribes of Israel | Jewish Virtual Library". jewishvirtuallibrary.org. Retrieved 2015-05-18.
- ^ Gen. 49:16 earliest reference among others
- ^ History of Phoenicia, by George Rawlinson 1889, "Phoenicia under the hegemony of Tyre (B.C. 1252–877)"
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v Sanders, E. P. (1993). The Historical Figure of Jesus. London, England, New York City, New York, Ringwood, Australia, Toronto, Ontario, and Auckland, New Zealand: Penguin Books. pp. 20–22. ISBN 978-0-14-014499-4.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Casey, Maurice (2010). Jesus of Nazareth: An Independent Historian's Account of His Life and Teaching. New York City, New York and London, England: T & T Clark. pp. 164–169. ISBN 978-0-567-64517-3.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- ^ "releases/2007/11/071121100831". sciencedaily.com. Retrieved 2015-05-18.
- ^ Scharfstein, S. (2004). Jewish History and You. Ktav Pub Incorporated. p. 24. ISBN 9780881258066. Retrieved 2015-05-18.
- ^ Leibner, Uzi. "Settlement and Demography in Late Roman and Byzantine Eastern Galilee". Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - ^ Le Strange, Guy. (1890) Palestine Under the Moslems pp. 30–32.
- ^ "The Jewish Agency for Israel". jafi.org.il. Archived from the original on 2009-12-22. Retrieved 2015-05-18.
- ^ a b Ofer Petersburg (December 12, 2007). "Jewish population in Galilee declining". Ynet. Archived from the original on December 9, 2012. Retrieved 2008-02-01.
- ^ "30 settlements planned for Negev and Galilee". 2003-08-08. Retrieved 2008-01-19.
- ^ "Places To Visit In Israel". govisitisrae. Retrieved 2013-07-25.
- ^ "Galilee in Jesus' Time Was a Center of Change". Ancient History. Retrieved 2013-07-25.
- ^ Matthew Krieger (November 19, 2007). "Gov't expected to join financing of huge northern development project". The Jerusalem Post. Archived from the original on August 13, 2011. Retrieved 2007-11-20.
- ^ Israel Central Bureau of Statistics (2013). "Localities and Population, by Group, District, Sub-district and Natural Region". Statistical Abstract of Israel (PDF) (Report). Retrieved 2014-06-16.
- ^ "In Galilee, Israeli Arabs finding greener grass in Jewish areas". Jewish Telegraphic Agency. Nov 3, 2008. Retrieved 2013-07-25.
- ^ Israel Central Bureau of Statistics (2013). "Sources of Population Growth, by District, Population Group and Religion". Statistical Abstract of Israel (PDF) (Report). Retrieved 2014-06-16.
- ^ Israel Central Bureau of Statistics (2002). The Arab Population in Israel (PDF) (Report). Statistilite. 27. sec. 23. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-09-23. Retrieved 2014-06-15.
- ^ "Haredim 'taking over'". Israel Business, ynetnews.com. 23 February 2011. Retrieved 2015-05-18.
- ^ Daniel Estrin, Canadian Press (April 15, 2011). "Israel unveils hiking trail in Galilee for Christian pilgrims". Yahoo! News. Archived from the original on 2013-03-13. Retrieved 2011-05-16.
- ^ "Acco Festival". accofestival.co.il. Archived from the original on 2015-07-02. Retrieved 2015-05-18.
![]() This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Easton, Matthew George (1897). . Easton's Bible Dictionary (New and revised ed.). T. Nelson and Sons.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Easton, Matthew George (1897). . Easton's Bible Dictionary (New and revised ed.). T. Nelson and Sons.
Further reading
- Aviam, M., "Galilee: The Hellenistic to Byzantine Periods," in The New Encyclopedia of Archaeological Excavations in the Holy Land, vol. 2 (4 vols) (Jerusalem: IES / Carta), 1993, 452–58.
- Meyers, Eric M. (ed), Galilee through the Centuries: Confluence of Cultures (Winona Lake, IN: Eisenbrauns, 1999) (Duke Judaic Studies 1).
- Chancey, A.M., Myth of a Gentile Galilee: The Population of Galilee and New Testament Studies (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2002) (Society of New Testament Monograph Series 118).
- Aviam, M., "First-century Jewish Galilee: An archaeological perspective," in Edwards, D.R. (ed.), Religion and Society in Roman Palestine: Old Questions, New Approaches (New York / London: Routledge, 2004), 7–27.
- Aviam, M., Jews, Pagans and Christians in the Galilee (Rochester NY: University of Rochester Press, 2004) (Land of Galilee 1).
- Chancey, Mark A., Greco-Roman Culture and the Galilee of Jesus (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2006) (Society for New Testament Studies Monograph Series, 134).
- Freyne, Sean, "Galilee and Judea in the First Century," in Margaret M. Mitchell and Frances M. Young (eds), Cambridge History of Christianity. Vol. 1. Origins to Constantine (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2006) (Cambridge History of Christianity), 163–94.
- Zangenberg, Jürgen, Harold W. Attridge and Dale B. Martin (eds), Religion, Ethnicity and Identity in Ancient Galilee: A Region in Transition (Tübingen, Mohr Siebeck, 2007) (Wissenschaftliche Untersuchungen zum Neuen Testament, 210).
- Fiensy, David A., "Population, Architecture, and Economy in Lower Galilean Villages and Towns in the First Century AD: A Brief Survey," in John D. Wineland, Mark Ziese, James Riley Estep Jr. (eds), My Father's World: Celebrating the Life of Reuben G. Bullard (Eugene (OR), Wipf & Stock, 2011), 101–19.
- Safrai, Shmuel, "The Jewish Cultural Nature of Galilee in the First Century" The New Testament and Christian–Jewish Dialogue: Studies in Honor of David Flusser, Immanuel 24/25 (1990): 147–86; electronically published on jerusalemperspective.com.