Akkadian Empire
Coordinates: 33°6′N 44°6′E / 33.100°N 44.100°E
Akkadian Empire | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c. 2334 – 2154 BC | |||||||||||||||||
![Bronze head of an Akkadian ruler, discovered in Nineveh in 1931, presumably depicting either Sargon or, more probably, Sargon's grandson Naram-Sin.[1] Reproduction in the Roemer- und Pelizaeus-Museum Hildesheim, the original from the National Museum of Iraq having been lost in the 2003 lootings.[2][1]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b1/Sargon_of_Akkad_%28frontal%29.jpg/250px-Sargon_of_Akkad_%28frontal%29.jpg) Bronze head of an Akkadian ruler, discovered in Nineveh in 1931, presumably depicting either Sargon or, more probably, Sargon's grandson Naram-Sin.[1] Reproduction in the Roemer- und Pelizaeus-Museum Hildesheim, the original from the National Museum of Iraq having been lost in the 2003 lootings.[2][1] | |||||||||||||||||
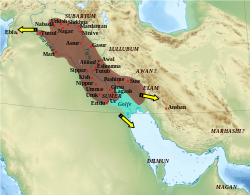 Map of the Akkadian Empire (brown) and the directions in which military campaigns were conducted (yellow arrows) | |||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Akkad | ||||||||||||||||
| Official languages | |||||||||||||||||
| Common languages | Akkadian Sumerian (declining) | ||||||||||||||||
| Religion | Ancient Mesopotamian religion | ||||||||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||||||||
| Šarrum | |||||||||||||||||
• c. 2334–2279 BC | Sargon (first) | ||||||||||||||||
• c. 2170–2154 BC | Shu-turul (last) | ||||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Bronze Age | ||||||||||||||||
• Established | c. 2334 BC | ||||||||||||||||
| c. 2340 – 2284 BC | |||||||||||||||||
• Disestablished | c. 2154 BC | ||||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||||
| 2350 BC[3] | 30,000 km2 (12,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||
| 2300 BC[3] | 650,000 km2 (250,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||
| 2250 BC[3] | 800,000 km2 (310,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||
| 2200 BC[3] | 250,000 km2 (97,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
The Akkadian Empire (/əˈkeɪdiən/)[4] was the first ancient empire of Mesopotamia, centered in the city of Akkad /ˈækæd/[5] and its surrounding region, which the Bible also called Akkad. The empire united Akkadian and Sumerian speakers under one rule. The Akkadian Empire exercised influence across Mesopotamia, the Levant, and Anatolia, sending military expeditions as far south as Dilmun and Magan (modern Bahrain and Oman) in the Arabian Peninsula.[6]
During the 3rd millennium BC, there developed a cultural symbiosis between the Sumerians and the Akkadians, which included widespread bilingualism.[7] Akkadian, an East Semitic language,[8] gradually replaced Sumerian as a spoken language somewhere between the 3rd and the 2nd millennia BC (the exact dating being a matter of debate).[9]
The Akkadian Empire reached its political peak between the 24th and 22nd centuries BC, following the conquests by its founder Sargon of Akkad.[10] Under Sargon and his successors, the Akkadian language was briefly imposed on neighboring conquered states such as Elam and Gutium. Akkad is sometimes regarded as the first empire in history, though the meaning of this term is not precise, and there are earlier Sumerian claimants.[11][12]
After the fall of the Akkadian Empire, the people of Mesopotamia eventually coalesced into two major Akkadian-speaking nations: Assyria in the north, and, a few centuries later, Babylonia in the south.
History of research[edit]
The Bible refers to Akkad as The Great City in Genesis 10:10–12, which states:
- "The beginning of his [Nimrod's] kingdom was Babel, and Erech, and Accad, and Calneh, in the land of Shinar. Out of that land he went forth into Assyria, and builded Nineveh, and Rehoboth-Ir, and Calah, and Resen between Nineveh and Calah (the same is the great city)."[13]
Nimrod's historical identity is unknown or debated, but Nimrod has been identified as Sargon of Akkad by some,[14] and others have compared him with the legendary Gilgamesh, founder of Uruk.[15][16] Today, scholars have documented some 7,000 texts from the Akkadian period, written in both Sumerian and Akkadian. Many later texts from the successor states of Assyria and Babylonia also deal with the Akkadian Empire.[16]
Understanding of the Akkadian Empire continues to be hampered by the fact that its capital Akkad has not yet been located, despite numerous attempts.[17][18] Precise dating of archaeological sites is hindered by the fact that there are no clear distinctions between artifact assemblages thought to stem from the preceding Early Dynastic period, and those thought to be Akkadian. Likewise, material that is thought to be Akkadian continues to be in use into the Ur III period.[19]
Many of the more recent insights on the Akkadian Empire have come from excavations in the Upper Khabur area in modern northeastern Syria which was to become a part of Assyria after the fall of Akkad. For example, excavations at Tell Mozan (ancient Urkesh) brought to light a sealing of Tar'am-Agade, a previously unknown daughter of Naram-Sin, who was possibly married to an unidentified local endan (ruler).[20] The excavators at nearby Tell Leilan (ancient Shekhna/Shubat-Enlil) have used the results from their investigations to argue that the Akkadian Empire came to an end due to a sudden drought, the so-called 4.2 kiloyear event.[21] The impact of this climate event on Mesopotamia in general, and on the Akkadian Empire in particular, continues to be hotly debated.[22]
Excavation at the modern site of Tell Brak has suggested that the Akkadians rebuilt a city ("Brak" or "Nagar") on this site, for use as an administrative center. The city included two large buildings including a complex with temple, offices, courtyard, and large ovens.[23][24]
Dating and periodization[edit]
The Akkadian Period is generally dated to either: c. 2334 BC – c. 2154 BC (according to the middle chronology timeline of the Ancient Near East), or c. 2270 BC – c. 2083 BC (according to the short chronology timeline of the Ancient Near East.) It was preceded by the Early Dynastic Period of Mesopotamia (ED) and succeeded by the Ur III Period, although both transitions are blurry. For example: it is likely that the rise of Sargon of Akkad coincided with the late ED Period and that the final Akkadian kings ruled simultaneously with the Gutian kings alongside rulers at the city-states of both: Uruk and Lagash. The Akkadian Period is contemporary with: EB IV (in Israel), EB IVA and EJ IV (in Syria), and EB IIIB (in Turkey.)[16][25]
Timeline of rulers[edit]
The relative order of Akkadian kings is clear. The absolute dates of their reigns are approximate (as with all dates prior to the late Bronze Age collapse c. 1200 BC).[26]
| Ruler | Middle Chronology All dates BC |
Family tree | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sargon | 2334–2279 | 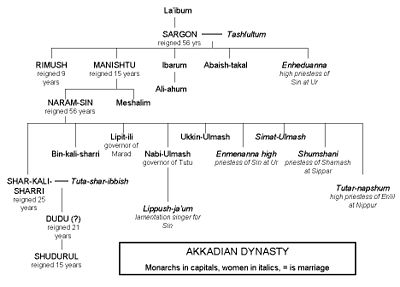
| |
| Rimush | 2278–2270 | ||
| Manishtushu | 2269–2255 | ||
| Naram-Sin | 2254–2218 | ||
| Shar-Kali-Sharri | 2217–2193 | ||
| Dudu | 2189–2169 | ||
| Shu-turul | 2168–2154 |
History and development of the empire[edit]
Pre-Sargonic Akkad[edit]


The Akkadian Empire takes its name from the region and the city of Akkad, both of which were localized in the general confluence area of the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. Although the city of Akkad has not yet been identified on the ground, it is known from various textual sources. Among these is at least one text predating the reign of Sargon. Together with the fact that the name Akkad is of non-Akkadian origin, this suggests that the city of Akkad may have already been occupied in pre-Sargonic times.[17][30]
Sargon of Akkad[edit]
Sargon of Akkad defeated and captured Lugal-zage-si in the Battle of Uruk and conquered his empire. The earliest records in the Akkadian language date to the time of Sargon. Sargon was claimed to be the son of La'ibum or Itti-Bel, a humble gardener, and possibly a hierodule, or priestess to Ishtar or Inanna. One legend related to Sargon in Assyrian times says that
My mother was a changeling, my father I knew not. The brothers of my father loved the hills. My city is Azurpiranu (the wilderness herb fields), which is situated on the banks of the Euphrates. My changeling mother conceived me, in secret she bore me. She set me in a basket of rushes, with bitumen she sealed my lid. She cast me into the river which rose not over me. The river bore me up and carried me to Akki, the drawer of water. Akki, the drawer of water, took me as his son and reared me. Akki the drawer of water, appointed me as his gardener. While I was gardener Ishtar granted me her love, and for four and (fifty?) ... years I exercised kingship.[31]
Later claims made on behalf of Sargon were that his mother was an "entu" priestess (high priestess). The claims might have been made to ensure a pedigree of nobility, since only a highly placed family could achieve such a position.[32]
Originally a cupbearer (Rabshakeh) to a king of Kish with a Semitic name, Ur-Zababa, Sargon thus became a gardener, responsible for the task of clearing out irrigation canals. The royal cupbearer at this time was in fact a prominent political position, close to the king and with various high level responsibilities not suggested by the title of the position itself.[33] This gave him access to a disciplined corps of workers, who also may have served as his first soldiers. Displacing Ur-Zababa, Sargon was crowned king, and he entered upon a career of foreign conquest.[34] Four times he invaded Syria and Canaan, and he spent three years thoroughly subduing the countries of "the west" to unite them with Mesopotamia "into a single empire".
However, Sargon took this process further, conquering many of the surrounding regions to create an empire that reached westward as far as the Mediterranean Sea and perhaps Cyprus (Kaptara); northward as far as the mountains (a later Hittite text asserts he fought the Hattian king Nurdaggal of Burushanda, well into Anatolia); eastward over Elam; and as far south as Magan (Oman) — a region over which he reigned for purportedly 56 years, though only four "year-names" survive. He consolidated his dominion over his territories by replacing the earlier opposing rulers with noble citizens of Akkad, his native city where loyalty would thus be ensured.[35]

Trade extended from the silver mines of Anatolia to the lapis lazuli mines in modern Afghanistan, the cedars of Lebanon and the copper of Magan. This consolidation of the city-states of Sumer and Akkad reflected the growing economic and political power of Mesopotamia. The empire's breadbasket was the rain-fed agricultural system of Assyria and a chain of fortresses was built to control the imperial wheat production.
Images of Sargon were erected on the shores of the Mediterranean, in token of his victories, and cities and palaces were built at home with the spoils of the conquered lands. Elam and the northern part of Mesopotamia (Assyria/Subartu) were also subjugated, and rebellions in Sumer were put down. Contract tablets have been found dated in the years of the campaigns against Canaan and against Sarlak, king of Gutium. He also boasted of having subjugated the "four-quarters" — the lands surrounding Akkad to the north (Assyria), the south (Sumer), the east (Elam), and the west (Martu). Some of the earliest historiographic texts (ABC 19, 20) suggest he rebuilt the city of Babylon (Bab-ilu) in its new location near Akkad.[39]
Sargon, throughout his long life, showed special deference to the Sumerian deities, particularly Inanna (Ishtar), his patroness, and Zababa, the warrior god of Kish. He called himself "The anointed priest of Anu" and "the great ensi of Enlil" and his daughter, Enheduanna, was installed as priestess to Nanna at the temple in Ur.
Troubles multiplied toward the end of his reign. A later Babylonian text states:
In his old age, all the lands revolted against him, and they besieged him in Akkad (the city) [but] he went forth to battle and defeated them, he knocked them over and destroyed their vast army.
It refers to his campaign in "Elam", where he defeated a coalition army led by the King of Awan and forced the vanquished to become his vassals.[40]
Also shortly after, another revolt took place:
the Subartu (mountainous tribes of Assyria) the upper country—in their turn attacked, but they submitted to his arms, and Sargon settled their habitations, and he smote them grievously.
Rimush and Manishtushu[edit]

Sargon had crushed opposition even at old age. These difficulties broke out again in the reign of his sons, where revolts broke out during the nine-year reign of Rimush (2278–2270 BC), who fought hard to retain the empire, and was successful until he was assassinated by some of his own courtiers. According to his inscriptions, he faced widespread revolts, and had to reconquer the cities of Ur, Umma, Adab, Lagash, Der, and Kazallu from rebellious ensis:[42] Rimush introduced mass slaughter and large scale destruction of the Sumerian city-states, and maintained meticulous records of his destructions.[43] Most of the major Sumerian cities were destroyed, and Sumerian human losses were enormous:[43][44]
| Sumerian casualties from the campaigns of Rimush[43] | ||||||
| Destroyed cities: | Adab and Zabala | Umma and KI.AN | Ur and Lagash | Kazallu | (Three battles in Sumer) | TOTAL |
| Killed | 15,718 | 8,900 | 8,049 | 12,052 | 11,322 | 56,041 |
| Captured and enslaved | 14,576 | 3,540 | 5,460 | 5,862 | _ | 29,438 |
| "Expelled and annihilated" | _ | 5,600 | 5,985 | _ | 14,100 | 25,685 |
| Total casualties | 111,164 | |||||
Rimush's elder brother, Manishtushu (2269–2255 BC) succeeded him. The latter seems to have fought a sea battle against 32 kings who had gathered against him and took control over their pre-Arab country, consisting of modern-day United Arab Emirates and Oman. Despite the success, like his brother he seems to have been assassinated in a palace conspiracy.[45][43]
Naram-Sin[edit]
Manishtushu's son and successor, Naram-Sin (2254–2218 BC), due to vast military conquests, assumed the imperial title "King Naram-Sin, king of the four-quarters" (Lugal Naram-Sîn, Šar kibrat 'arbaim), the four-quarters as a reference to the entire world. He was also for the first time in Sumerian culture, addressed as "the god (Sumerian = DINGIR, Akkadian = ilu) of Agade" (Akkad), in opposition to the previous religious belief that kings were only representatives of the people towards the gods.[46][47] He also faced revolts at the start of his reign,[48] but quickly crushed them.

Naram-Sin also recorded the Akkadian conquest of Ebla as well as Armanum and its king.[50] The location of Armanum is debated: it is sometimes identified with a Syrian kingdom mentioned in the tablets of Ebla as Armi, whose location is also debated; while historian Adelheid Otto identifies it with the Citadel of Bazi at the Tell Banat complex on the Euphrates River between Ebla and Tell Brak,[51][50] others like Wayne Horowitz identify it with Aleppo.[52] Further, while most scholars place Armanum in Syria, Michael C. Astour believes it to be located north of the Hamrin Mountains in northern Iraq.[53]
To better police Syria, he built a royal residence at Tell Brak, a crossroads at the heart of the Khabur River basin of the Jezirah. Naram-Sin campaigned against Magan which also revolted; Naram-Sin "marched against Magan and personally caught Mandannu, its king", where he instated garrisons to protect the main roads. The chief threat seemed to be coming from the northern Zagros Mountains, the Lulubis and the Gutians. A campaign against the Lullubi led to the carving of the "Victory Stele of Naram-Suen", now in the Louvre. Hittite sources claim Naram-Sin of Akkad even ventured into Anatolia, battling the Hittite and Hurrian kings Pamba of Hatti, Zipani of Kanesh, and 15 others. This newfound Akkadian wealth may have been based upon benign climatic conditions, huge agricultural surpluses and the confiscation of the wealth of other peoples.[54]
The economy was highly planned. Grain was cleaned, and rations of grain and oil were distributed in standardized vessels made by the city's potters. Taxes were paid in produce and labour on public walls, including city walls, temples, irrigation canals and waterways, producing huge agricultural surpluses.[55]
In later Assyrian and Babylonian texts, the name Akkad, together with Sumer, appears as part of the royal title, as in the Sumerian LUGAL KI-EN-GI KI-URI or Akkadian Šar māt Šumeri u Akkadi,[56] translating to "king of Sumer and Akkad".[57] This title was assumed by the king who seized control of Nippur,[56] the intellectual and religious center of southern Mesopotamia.
During the Akkadian period, the Akkadian language became the lingua franca of the Middle East, and was officially used for administration, although the Sumerian language remained as a spoken and literary language. The spread of Akkadian stretched from Syria to Elam, and even the Elamite language was temporarily written in Mesopotamian cuneiform. Akkadian texts later found their way to far-off places, from Egypt (in the Amarna Period) and Anatolia, to Persia (Behistun).
Submission of Sumerian kings[edit]
The submission of some Sumerian rulers to the Akkadian Empire, is recorded in the seal inscriptions of Sumerian rulers such as Lugal-ushumgal, governor (ensi) of Lagash ("Shirpula"), circa 2230-2210 BCE. Several inscriptions of Lugal-ushumgal are known, particularly seal impressions, which refer to him as governor of Lagash and at the time a vassal (𒀵, arad, "servant" or "slave") of Naram-Sin, as well as his successor Shar-kali-sharri.[58][59][60][61][62] One of these seals proclaims:
“Naram-Sin, the mighty God of Agade, king of the four corners of the world, Lugalushumgal, the scribe, ensi of Lagash, is thy servant.”
It can be considered that Lugalushumgal was a collaborator of the Akkadian Empire, as was Meskigal, ruler of Adab.[64] Later however, Lugal-ushumgal was succeeded by Puzer-Mama who, as Akkadian power waned, achieved independence from Shar-Kali-Sharri, assuming the title of "King of Lagash" and starting the illustrious Second Dynasty of Lagash.[65][66]
Collapse[edit]

The empire of Akkad fell, perhaps in the 22nd century BC, within 180 years of its founding, ushering in a "Dark Age" with no prominent imperial authority until Third Dynasty of Ur. The region's political structure may have reverted to the status quo ante of local governance by city-states.[67]
Shu-turul appears to have restored some centralized authority, however, he was unable to prevent the empire eventually collapsing outright from the invasion of barbarian peoples from the Zagros Mountains known as the Gutians.
Little is known about the Gutian period, or how long it endured. Cuneiform sources suggest that the Gutians' administration showed little concern for maintaining agriculture, written records, or public safety; they reputedly released all farm animals to roam about Mesopotamia freely and soon brought about famine and rocketing grain prices. The Sumerian king Ur-Nammu (2112–2095 BC) cleared the Gutians from Mesopotamia during his reign.
The Sumerian King List, describing the Akkadian Empire after the death of Shar-kali-shari, states:
Who was king? Who was not king? Irgigi the king; Nanum, the king; Imi the king; Ilulu, the king—the four of them were kings but reigned only three years. Dudu reigned 21 years; Shu-Turul, the son of Dudu, reigned 15 years. ... Agade was defeated and its kingship carried off to Uruk. In Uruk, Ur-ningin reigned 7 years, Ur-gigir, son of Ur-ningin, reigned 6 years; Kuda reigned 6 years; Puzur-ili reigned 5 years, Ur-Utu reigned 6 years. Uruk was smitten with weapons and its kingship carried off by the Gutian hordes.
However, there are no known year-names or other archaeological evidence verifying any of these later kings of Akkad or Uruk, apart from several artefact referencing king Dudu of Akkad and Shu-turul.[68] The named kings of Uruk may have been contemporaries of the last kings of Akkad, but in any event could not have been very prominent.
In the Gutian hordes, (first reigned) a nameless king; (then) Imta reigned 3 years as king; Shulme reigned 6 years; Elulumesh reigned 6 years; Inimbakesh reigned 5 years; Igeshuash reigned 6 years; Iarlagab reigned 15 years; Ibate reigned 3 years; ... reigned 3 years; Kurum reigned 1 year; ... reigned 3 years; ... reigned 2 years; Iararum reigned 2 years; Ibranum reigned 1 year; Hablum reigned 2 years; Puzur-Sin son of Hablum reigned 7 years; Iarlaganda reigned 7 years; ... reigned 7 years; ... reigned 40 days. Total 21 kings reigned 91 years, 40 days.

The period between c. 2112 BC and 2004 BC is known as the Ur III period. Documents again began to be written in Sumerian, although Sumerian was becoming a purely literary or liturgical language, much as Latin later would be in Medieval Europe.[31]
One explanation for the end of the Akkadian empire is simply that the Akkadian dynasty could not maintain its political supremacy over other independently powerful city-states.[67][70]
Drought[edit]
One theory associates regional decline at the end of the Akkadian period (and of the First Intermediary Period following the Old Kingdom in Ancient Egypt) was associated with rapidly increasing aridity, and failing rainfall in the region of the Ancient Near East, caused by a global centennial-scale drought.[71][72] Harvey Weiss has shown that
[A]rchaeological and soil-stratigraphic data define the origin, growth, and collapse of Subir, the third millennium rain-fed agriculture civilization of northern Mesopotamia on the Habur Plains of Syria. At 2200 BC, a marked increase in aridity and wind circulation, subsequent to a volcanic eruption, induced a considerable degradation of land-use conditions. After four centuries of urban life, this abrupt climatic change evidently caused abandonment of Tell Leilan, regional desertion, and the collapse of the Akkadian empire based in southern Mesopotamia. Synchronous collapse in adjacent regions suggests that the impact of the abrupt climatic change was extensive.[21]
Peter B. deMenocal has shown "there was an influence of the North Atlantic Oscillation on the streamflow of the Tigris and Euphrates at this time, which led to the collapse of the Akkadian Empire".[73] More recent analysis of simulations from the HadCM3 climate model indicate that there was a shift to a more arid climate on a timescale that is consistent with the collapse of the empire.[74]

Excavation at Tell Leilan suggests that this site was abandoned soon after the city's massive walls were constructed, its temple rebuilt and its grain production reorganized. The debris, dust, and sand that followed show no trace of human activity. Soil samples show fine wind-blown sand, no trace of earthworm activity, reduced rainfall and indications of a drier and windier climate. Evidence shows that skeleton-thin sheep and cattle died of drought, and up to 28,000 people abandoned the site, seeking wetter areas elsewhere. Tell Brak shrank in size by 75%. Trade collapsed. Nomadic herders such as the Amorites moved herds closer to reliable water suppliers, bringing them into conflict with Akkadian populations. This climate-induced collapse seems to have affected the whole of the Middle East, and to have coincided with the collapse of the Egyptian Old Kingdom.[21]
This collapse of rain-fed agriculture in the Upper Country meant the loss to southern Mesopotamia of the agrarian subsidies which had kept the Akkadian Empire solvent. Water levels within the Tigris and Euphrates fell 1.5 meters beneath the level of 2600 BC, and although they stabilized for a time during the following Ur III period, rivalries between pastoralists and farmers increased. Attempts were undertaken to prevent the former from herding their flocks in agricultural lands, such as the building of a 180 km (112 mi) wall known as the "Repeller of the Amorites" between the Tigris and Euphrates under the Ur III ruler Shu-Sin. Such attempts led to increased political instability; meanwhile, severe depression occurred to re-establish demographic equilibrium with the less favorable climatic conditions.[78][79][80]
Richard Zettler has critiqued the drought theory, observing that the chronology of the Akkadian empire is very uncertain and that available evidence is not sufficient to show its economic dependence on the northern areas excavated by Weiss and others. He also criticizes Weiss for taking Akkadian writings literally to describe certain catastrophic events.[81]
According to Joan Oates, at Tell Brak, the soil "signal" associated with the drought lies below the level of Naram-Sin's palace. However, evidence
may suggest a tightening of Akkadian control following the Brak 'event', for example, the construction of the heavily fortified 'palace' itself and the apparent introduction of greater numbers of Akkadian as opposed to local officials, perhaps a reflection of unrest in the countryside of the type that often follows some natural catastrophe.
Furthermore, Brak remained occupied and functional after the fall of the Akkadians.[82]
In 2019, a study by Hokkaido University on fossil corals in Oman provides an evidence that prolonged winter shamal seasons led to the salinization of the irrigated fields; hence, a dramatic decrease in crop production triggered a widespread famine and eventually the collapse of the ancient Akkadian Empire.[83][84]
Government[edit]

The Akkadian government formed a "classical standard" with which all future Mesopotamian states compared themselves. Traditionally, the ensi was the highest functionary of the Sumerian city-states. In later traditions, one became an ensi by marrying the goddess Inanna, legitimising the rulership through divine consent.
Initially, the monarchical lugal (lu = man, gal =Great) was subordinate to the priestly ensi, and was appointed at times of troubles, but by later dynastic times, it was the lugal who had emerged as the preeminent role, having his own "é" (= house) or "palace", independent from the temple establishment. By the time of Mesalim, whichever dynasty controlled the city of Kish was recognised as šar kiššati (= king of Kish), and was considered preeminent in Sumer, possibly because this was where the two rivers approached, and whoever controlled Kish ultimately controlled the irrigation systems of the other cities downstream.
As Sargon extended his conquest from the "Lower Sea" (Persian Gulf), to the "Upper Sea" (Mediterranean), it was felt that he ruled "the totality of the lands under heaven", or "from sunrise to sunset", as contemporary texts put it. Under Sargon, the ensis generally retained their positions, but were seen more as provincial governors. The title šar kiššati became recognised as meaning "lord of the universe". Sargon is even recorded as having organised naval expeditions to Dilmun (Bahrain) and Magan, amongst the first organised military naval expeditions in history. Whether he also did in the case of the Mediterranean with the kingdom of Kaptara (possibly Cyprus), as claimed in later documents, is more questionable.
With Naram-Sin, Sargon's grandson, this went further than with Sargon, with the king not only being called "Lord of the Four-Quarters (of the Earth)", but also elevated to the ranks of the dingir (= gods), with his own temple establishment. Previously a ruler could, like Gilgamesh, become divine after death but the Akkadian kings, from Naram-Sin onward, were considered gods on earth in their lifetimes. Their portraits showed them of larger size than mere mortals and at some distance from their retainers.[85]
One strategy adopted by both Sargon and Naram-Sin, to maintain control of the country, was to install their daughters, Enheduanna and Emmenanna respectively, as high priestess to Sin, the Akkadian version of the Sumerian moon deity, Nanna, at Ur, in the extreme south of Sumer; to install sons as provincial ensi governors in strategic locations; and to marry their daughters to rulers of peripheral parts of the Empire (Urkesh and Marhashe). A well documented case of the latter is that of Naram-Sin's daughter Tar'am-Agade at Urkesh.[86]
Records at the Brak administrative complex suggest that the Akkadians appointed locals as tax collectors.[87]
Economy[edit]
The population of Akkad, like nearly all pre-modern states, was entirely dependent upon the agricultural systems of the region, which seem to have had two principal centres: the irrigated farmlands of southern Iraq that traditionally had a yield of 30 grains returned for each grain sown and the rain-fed agriculture of northern Iraq, known as the "Upper Country."
Southern Iraq during Akkadian period seems to have been approaching its modern rainfall level of less than 20 mm (0.8 in) per year, with the result that agriculture was totally dependent upon irrigation. Before the Akkadian period the progressive salinisation of the soils, produced by poorly drained irrigation, had been reducing yields of wheat in the southern part of the country, leading to the conversion to more salt-tolerant barley growing. Urban populations there had peaked already by 2,600 BC, and demographic pressures were high, contributing to the rise of militarism apparent immediately before the Akkadian period (as seen in the Stele of the Vultures of Eannatum). Warfare between city states had led to a population decline, from which Akkad provided a temporary respite.[89] It was this high degree of agricultural productivity in the south that enabled the growth of the highest population densities in the world at this time, giving Akkad its military advantage.

The water table in this region was very high and replenished regularly—by winter storms in the headwaters of the Tigris and Euphrates from October to March and from snow-melt from March to July. Flood levels, that had been stable from about 3,000 to 2,600 BC, had started falling, and by the Akkadian period were a half-meter to a meter lower than recorded previously. Even so, the flat country and weather uncertainties made flooding much more unpredictable than in the case of the Nile; serious deluges seem to have been a regular occurrence, requiring constant maintenance of irrigation ditches and drainage systems. Farmers were recruited into regiments for this work from August to October—a period of food shortage—under the control of city temple authorities, thus acting as a form of unemployment relief. Gwendolyn Leick has[90] suggested that this was Sargon's original employment for the king of Kish, giving him experience in effectively organising large groups of men; a tablet reads, "Sargon, the king, to whom Enlil permitted no rival—5,400 warriors ate bread daily before him".[91]
Harvest was in the late spring and during the dry summer months. Nomadic Amorites from the northwest would pasture their flocks of sheep and goats to graze on the crop residue and be watered from the river and irrigation canals. For this privilege, they would have to pay a tax in wool, meat, milk, and cheese to the temples, who would distribute these products to the bureaucracy and priesthood. In good years, all would go well, but in bad years, wild winter pastures would be in short supply, nomads would seek to pasture their flocks in the grain fields, and conflicts with farmers would result. It would appear that the subsidizing of southern populations by the import of wheat from the north of the Empire temporarily overcame this problem,[92] and it seems to have allowed economic recovery and a growing population within this region.
Foreign trade[edit]
As a result, Sumer and Akkad had a surplus of agricultural products but was short of almost everything else, particularly metal ores, timber and building stone, all of which had to be imported. The spread of the Akkadian state as far as the "silver mountain" (possibly the Taurus Mountains), the "cedars" of Lebanon, and the copper deposits of Magan, was largely motivated by the goal of securing control over these imports. One tablet reads:
"Sargon, the king of Kish, triumphed in thirty-four battles (over the cities) up to the edge of the sea (and) destroyed their walls. He made the ships from Meluhha, the ships from Magan (and) the ships from Dilmun tie up alongside the quay of Agade. Sargon the king prostrated himself before (the god) Dagan (and) made supplication to him; (and) he (Dagan) gave him the upper land, namely Mari, Yarmuti, (and) Ebla, up to the Cedar Forest (and) up to the Silver Mountain"
International trade developed during the Akkadian period. Indus-Mesopotamia relations also seem to have expanded: Sargon of Akkad (circa 2300 or 2250 BC), was the first Mesopotamian ruler to make an explicit reference to the region of Meluhha, which is generally understood as being the Baluchistan or the Indus area.[95]
Culture[edit]
Art[edit]
In art, there was a great emphasis on the kings of the dynasty, alongside much that continued earlier Sumerian art. Little architecture remains. In large works and small ones such as seals, the degree of realism was considerably increased,[98] but the seals show a "grim world of cruel conflict, of danger and uncertainty, a world in which man is subjected without appeal to the incomprehensible acts of distant and fearful divinities who he must serve but cannot love. This sombre mood ... remained characteristic of Mesopotamian art..."[99]
Akkadian sculpture is remarkable for its fineness and realism, which shows a clear advancement compared to the previous period of Sumerian art.[100][101]
Seals[edit]
The Akkadians used visual arts as a vehicle of ideology. They developed a new style for cylinder seals, by reusing traditional animal decorations but organizing them around inscriptions, which often became central parts of the layout. The figures also became more sculptural and naturalistic. New elements were also included, especially in relation to the rich Akkadian mythology.
Summer God and Dumuzi. Louvre Museum
Language[edit]
During the 3rd millennium BC, there developed a very intimate cultural symbiosis between the Sumerians and the Akkadians, which included widespread bilingualism.[7] The influence of Sumerian on Akkadian (and vice versa) is evident in all areas, from lexical borrowing on a massive scale, to syntactic, morphological, and phonological convergence.[7] This has prompted scholars to refer to Sumerian and Akkadian in the third millennium as a sprachbund.[7] Akkadian gradually replaced Sumerian as a spoken language somewhere around 2000 BC (the exact dating being a matter of debate),[9] but Sumerian continued to be used as a sacred, ceremonial, literary, and scientific language in Mesopotamia until the 1st century AD.[103]
Poet–priestess Enheduanna[edit]
Sumerian literature continued in rich development during the Akkadian period. Enheduanna, the "wife (Sumerian dam = high priestess) of Nanna [the Sumerian moon god] and daughter of Sargon"[104] of the temple of Sin at Ur, who lived c. 2285–2250 BC, is the first poet in history whose name is known. Her known works include hymns to the goddess Inanna, the Exaltation of Inanna and In-nin sa-gur-ra. A third work, the Temple Hymns, a collection of specific hymns, addresses the sacred temples and their occupants, the deity to whom they were consecrated. The works of this poet are significant, because although they start out using the third person, they shift to the first person voice of the poet herself, and they mark a significant development in the use of cuneiform. As poet, princess, and priestess, she was a person who, according to William W Hallo, "set standards in all three of her roles for many succeeding centuries"[105]
In the Exultation of Inanna,
Enheduanna depicts Inanna as disciplining mankind as a goddess of battle. She thereby unites the warlike Akkadian Ishtar's qualities to those of the gentler Sumerian goddess of love and fecundity. She likens Inanna to a great storm bird who swoops down on the lesser gods and sends them fluttering off like surprised bats. Then, in probably the most interesting part of the hymn, Enheduanna herself steps forward in the first person to recite her own past glories, establishing her credibility, and explaining her present plight. She has been banished as high priestess from the temple in the city of Ur and from Uruk and exiled to the steppe. She begs the moon god Nanna to intercede for her because the city of Uruk, under the ruler Lugalanne, has rebelled against Sargon. The rebel, Lugalanne, has even destroyed the temple Eanna, one of the greatest temples in the ancient world, and then made advances on his sister-in-law.[106]
Curse of Akkad[edit]

Later material described how the fall of Akkad was due to Naram-Sin's attack upon the city of Nipper. When prompted by a pair of inauspicious oracles, the king sacked the E-kur temple, supposedly protected by the god Enlil, head of the pantheon. As a result of this, eight chief deities of the Anunnaki pantheon were supposed to have come together and withdrawn their support from Akkad.[107]
- For the first time since cities were built and founded,
- The great agricultural tracts produced no grain,
- The inundated tracts produced no fish,
- The irrigated orchards produced neither syrup nor wine,
- The gathered clouds did not rain, the masgurum did not grow.
- At that time, one shekel's worth of oil was only one-half quart,
- One shekel's worth of grain was only one-half quart. . . .
- These sold at such prices in the markets of all the cities!
- He who slept on the roof, died on the roof,
- He who slept in the house, had no burial,
- People were flailing at themselves from hunger.
The kings of Akkad were legendary among later Mesopotamian civilizations, with Sargon understood as the prototype of a strong and wise leader, and his grandson Naram-Sin considered the wicked and impious leader (Unheilsherrscher in the analysis of Hans Gustav Güterbock) who brought ruin upon his kingdom.[108][109]
Technology[edit]

Tablets from the periods reads, "(From the earliest days) no-one had made a statue of lead, (but) Rimush king of Kish, had a statue of himself made of lead. It stood before Enlil; and it recited his (Rimush's) virtues to the idu of the gods". The copper Bassetki Statue, cast with the lost wax method, testifies to the high level of skill that craftsmen achieved during the Akkadian period.[110]
Achievements[edit]
The empire was bound together by roads, along which there was a regular postal service. Clay seals that took the place of stamps bear the names of Sargon and his son. A cadastral survey seems also to have been instituted, and one of the documents relating to it states that a certain Uru-Malik, whose name appears to indicate his Canaanite origin, was governor of the land of the Amorites, or Amurru as the semi-nomadic people of Syria and Canaan were called in Akkadian. It is probable that the first collection of astronomical observations and terrestrial omens was made for a library established by Sargon. The earliest "year names", whereby each year of a king's reign was named after a significant event performed by that king, date from Sargon's reign. Lists of these "year names" henceforth became a calendrical system used in most independent Mesopotamian city-states. In Assyria, however, years came to be named for the annual presiding limmu official appointed by the king, rather than for an event.
See also[edit]
Part of a series on the |
|---|
| History of Iraq |
 |
|
|
- Cities of the ancient Near East
- Religions of the ancient Near East
- History of Mesopotamia
- Timeline of the Assyrian Empire
Notes[edit]
- ^ a b Mallowan, M. E. L. (1936). "The Bronze Head of the Akkadian Period from Nineveh". Iraq. 3 (1): 104–110. JSTOR 4241589.
- ^ Kidner, Frank L.; Bucur, Maria; Mathisen, Ralph; McKee, Sally; Weeks, Theodore R. (2007). Making Europe: People, Politics, and Culture. Cengage Learning. p. 15. ISBN 978-0-618-00479-9.
- ^ a b c d Taagepera, Rein (1979). "Size and Duration of Empires: Growth-Decline Curves, 600 B.C. to 600 A.D.". Social Science History. 3 (3/4): 115–138. doi:10.2307/1170959. JSTOR 1170959.
- ^ Akkadian: URUAkkad KI; Hittite: KUR A.GA.DÈ.KI "land of Akkad"; Biblical Hebrew אַכַּד Akkad.
- ^ Sumerian: Agade
- ^ Mish, Frederick C., Editor in Chief. "Akkad" Webster’s Ninth New Collegiate Dictionary. ninth ed. Springfield, MA: Merriam-Webster 1985. ISBN 0-87779-508-8).
- ^ a b c d Deutscher, Guy (2007). Syntactic Change in Akkadian: The Evolution of Sentential Complementation. Oxford University Press US. pp. 20–21. ISBN 978-0-19-953222-3.
- ^ Hasselbach, Rebecca (2005). Sargonic Akkadian: A Historical and Comparative Study of the Syllabic Texts. Otto Harrassowitz Verlag. p. 2. ISBN 9783447051729.
- ^ a b Woods, C. (2006). "Bilingualism, Scribal Learning, and the Death of Sumerian" (PDF). S.L. Sanders (ed) Margins of Writing, Origins of Culture: 91–120. Chicago.
- ^ Zettler (2003), p. 20. "Brinkman's chronology places Sargon's accession at 2334, his successors, Naram-Suen and Sharkalisharri, under whom the dynasty presumably collapsed, at 2254–2218 and 2217–2193, respectively, and the Third Dynasty of Ur at 2112–2004. however, Brinkman noted that if Hallo's 40-year Gutian interregnum is correct then the Dynasty of Akkade would have to be dated 2293–2113. The middle chronology, however, is under attack, with various scholars arguing strongly in favor of a low(er) chronology and for various reasons. Without going into detail, Boese has placed Sargon's accession at shortly after 2250 (1982), Gasche, Armstrong, Cole and Gurzadyan at 2200 (1998) and Reade at 2180 (2001), with the Third Dynasty of Ur moved according."
- ^ F Leo Oppenhiem – Ancient Mesopotamia
- ^ Liverani (1993), p. 3. "The factual criticism is that empires existed even before Akkad: or more properly that the term and concept of 'empire' has been recently applied (on not worse grounds than in the case of Akkad) to other older cases, from the Uruk of the late-Uruk period to the Ebla of the royal archives, to the very state formations of the Sumerian south in the period called in fact 'proto-imperial'. In no case is the Akkad empire an absolute novelty [...] 'Akkad the first empire' is therefore subject to criticism not only as for the adjective 'first' but especially as for the noun 'empire'.
- ^ American Standard Version (1901)
- ^ Douglas N. Petrovich: "Identifying Nimrod of Genesis 10 with Sargon of Akkad by Exegetical and Archaeological Means", Journal of the Evangelical Theological Society, 2013. https://www.academia.edu/2184113/_2013_Identifying_Nimrod_of_Genesis_10_with_Sargon_of_Akkad_by_Exegetical_and_Archaeological_Means
- ^ Dalley, Stephanie (1997). The Legacy of Mesopotamia. New York: Oxford University Press. p. 116. ISBN 9780198149460.
- ^ a b c Schrakamp, Ingo (2013). "Sargon of Akkad and his dynasty". In Bagnall, Roger S. (ed.). The Encyclopedia of Ancient History. Chicago: Blackwell. pp. 6045–6047. doi:10.1002/9781444338386.wbeah24182. ISBN 9781444338386.
- ^ a b Wall-Romana, Christophe (1990). "An Areal Location of Agade". Journal of Near Eastern Studies. 49 (3): 205–245. doi:10.1086/373442. JSTOR 546244.
- ^ Weiss, Harvey (1975), "Kish, Akkad and Agade", Journal of the American Oriental Society, 95 (3): 434–453, doi:10.2307/599355, JSTOR 599355
- ^ McMahon, Augusta (2006). The Early Dynastic to Akkadian Transition. The Area WF Sounding at Nippur (PDF). Chicago: Oriental Institute. ISBN 978-1-885923-38-7. Retrieved 19 March 2015.
- ^ Buccellati, Giorgio; Kelly-Buccellati, Marilyn (2002). "Tar'am-Agade, Daughter of Naram-Sin, at Urkesh" (PDF). In Al-Gailani Werr, Lamia (ed.). Of Pots and Plans. Papers on the Archaeology and History of Mesopotamia and Syria presented to David Oates in Honour of his 75th Birthday. London: Nabu. pp. 11–31. ISBN 978-1897750629. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ^ a b c Weiss, H; et al. (1993). "The Genesis and Collapse of Third Millennium North Mesopotamian Civilization". Science. 261 (5124): 995–1004. Bibcode:1993Sci...261..995W. doi:10.1126/science.261.5124.995. PMID 17739617.
- ^ Wiener, Malcolm H. (2014). "The Interaction of Climate Change and Agency in the Collapse of Civilizations ca. 2300–2000 BC". Radiocarbon. 56 (4): S1–S16. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.692.2170. doi:10.2458/azu_rc.56.18325.
- ^ J. Oates (2004), pp. 5–8. "Following the destruction of the city sometime in the twenty-third century BC, Nagar was rebuilt by officials of the Akkadian Dynasty as a major centre of their provincial administration, a fact clearly attested in the cuneiform documents from this site."
- ^ Oates, David; Oates, Joan (1989). "Akkadian Buildings at Tell Brak". Iraq. 51: 193–211. doi:10.2307/4200303. JSTOR 4200303.
- ^ Pruß, Alexander (2004), "Remarks on the Chronological Periods", in Lebeau, Marc; Sauvage, Martin (eds.), Atlas of Preclassical Upper Mesopotamia, Subartu, 13, pp. 7–21, ISBN 978-2503991207
- ^ van de Mieroop, M. (2007). A History of the Ancient Near East, ca. 3000–323 BC. Malden: Blackwell. ISBN 978-0-631-22552-2.
- ^ a b Foster, Benjamin R. (2015). The Age of Agade: Inventing Empire in Ancient Mesopotamia. Routledge. p. 3. ISBN 9781317415527.
- ^ Nigro, Lorenzo (1998). "The Two Steles of Sargon: Iconology and Visual Propaganda at the Beginning of Royal Akkadian Relief". Iraq. British Institute for the Study of Iraq. 60: 92. JSTOR 4200454.
- ^ a b Nigro, Lorenzo (1998). "The Two Steles of Sargon: Iconology and Visual Propaganda at the Beginning of Royal Akkadian Relief". Iraq. British Institute for the Study of Iraq. 60: 93–94. JSTOR 4200454.
- ^ Foster, Benjamin R. (2013), "Akkad (Agade)", in Bagnall, Roger S. (ed.), The Encyclopedia of Ancient History, Chicago: Blackwell, pp. 266–267, doi:10.1002/9781444338386.wbeah01005, ISBN 9781444338386
- ^ a b Georges Roux (1996), Ancient Iraq (3rd Edition)(Penguin Harmondsworth)
- ^ Stiebing Jr, H. William (2009). Ancient Near Eastern History and Culture. Pearson Longman; University of New Orleans. p. 69.
- ^ Sargon, doi:10.1163/1574-9347_bnp_e1101500
- ^ Samuel Noah Kramer, The Sumerians, Chicago University Press, 1971, ISBN 0-226-45238-7
- ^ Stiebing Jr, H. William (2009). Ancient Near Eastern History and Culture. Pearson Longman; University of New Orleans. p. 70.
- ^ Potts, D. T. (1999). The Archaeology of Elam: Formation and Transformation of an Ancient Iranian State. Cambridge University Press. p. 104. ISBN 9780521564960.
- ^ Harper, Prudence O. (1992). Royal City of Susa: Ancient Near Eastern Treasures in the Louvre. Metropolitan Museum of Art. pp. 162–163.
- ^ Nigro, Lorenzo (1998). "The Two Steles of Sargon: Iconology and Visual Propaganda at the Beginning of Royal Akkadian Relief". Iraq. British Institute for the Study of Iraq. 60: 89 Note 14. JSTOR 4200454.
- ^ Dalley proposes that these sources may have originally referred to Sargon II of the Assyria rather than Sargon of Akkad. Stephanie Dalley, "Babylon as a Name for Other Cities Including Nineveh", in [1] Proceedings of the 51st Rencontre Assyriologique Internationale, Oriental Institute SAOC 62, pp. 25–33, 2005
- ^ Stiebing Jr, H. William (2009). Ancient Near Eastern History and Culture. Pearson Longman; University of New Orleans. p. 71.
- ^ "Musée du Louvre-Lens - Portail documentaire - Stèle de victoire du roi Rimush (?)". ressources.louvrelens.fr (in French).
- ^ Hamblin, William J. (2006). Warfare in the Ancient Near East to 1600 BC: Holy Warriors at the Dawn of History. Routledge. pp. 93–94. ISBN 978-1-134-52062-6.
- ^ a b c d Hamblin, William J. (2006). Warfare in the Ancient Near East to 1600 BC: Holy Warriors at the Dawn of History. Routledge. pp. 93–94. ISBN 978-1-134-52062-6.
- ^ Crowe, D. (2014). War Crimes, Genocide, and Justice: A Global History. Springer. p. 10. ISBN 978-1-137-03701-5.
- ^ Stiebing Jr, H. William (2009). Ancient Near Eastern History and Culture. Pearson Longman; University of New Orleans. p. 72.
- ^ a b Stiebing, H. William, Jr. (2009). Ancient Near Eastern History and Culture. Pearson Longman. p. 74. ISBN 978-0-321-42297-2.
- ^ Michalowski, Piotr (2008). "The Mortal Kings of Ur: A Short Century of Divine Rule in Ancient Mesopotamia" (PDF). Oriental Institute Seminars. 4. The Oriental Institute. pp. 33–45. ISBN 1-885923-55-4.
- ^ Tinney, Steve (1995). "A New Look at Naram-Sin and the Great Rebellion". Journal of Cuneiform Studies. 47: 1–14. doi:10.2307/1359810.
- ^ Stele of Narâm-Sîn, king of Akkad, celebrating his victory against the Lullubi from Zagros. Limestone, c. 2250 BCE. Brought from Sippar to Susa among other spoils of war in the 12th century BCE. Now given dates for Naram-Suen of Akkad, reign 2190 – 2154 BC.
- ^ a b Otto, Adelheid (2006). "Archaeological Perspectives on the Localization of Naram-Sin's Armanum". Journal of Cuneiform Studies. 58: 1–26. doi:10.1086/JCS40025220.
- ^ Foster, Benjamin R. (1982). "The Siege of Armanum". Journal of the Ancient Near Eastern Society. 14: 27–36.
- ^ Horowitz, Wayne; Horowitz, Alexandra (1998). Mesopotamian Cosmic Geography. ISBN 0-931464-99-4.
- ^ Cyrus Herzl Gordon; Gary Rendsburg; Nathan H. Winter (1987). Eblaitica: Essays on the Ebla Archives and Eblaite Language, Volume 4. pp. 63–66. ISBN 1-57506-060-4.
- ^ Burroughs, William J. (2008). Climate Change in Prehistory: The end of the age of chaos. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-07010-4.
- ^ Fagan, Brian (2004). The Long Summer: how climate changed civilisation. Granta Books. ISBN 1-86207-644-8.[page needed]
- ^ a b De Mieroop, Marc Van (2005). A History of the Ancient Near East ca. 3000–323 BC. Malden: Blackwell. ISBN 0-631-22552-8.
- ^ Prince, John Dyneley (1911). . In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). Encyclopædia Britannica. 1 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 457.
- ^ "Sumerian Dictionary". oracc.iaas.upenn.edu.
- ^ a b Radau, Hugo (2005). Early Babylonian History: Down to the End of the Fourth Dynasty of Ur. Wipf and Stock Publishers. pp. 6–7. ISBN 978-1-59752-381-3.
- ^ Woolley, Leonard (1938). The Summerians. p. 83.
- ^ The Art Of Ancient Mesopotamia ( Art Ebook). p. 53.
- ^ Seal image M4 in: The Art Of Ancient Mesopotamia ( Art Ebook). p. 53.
- ^ "CDLI-Archival View RT 165". cdli.ucla.edu.
- ^ The Cambridge Ancient History. Cambridge University Press. 1971. p. 436.
- ^ "Puzur-Mama, who served as a “governor” of Lagash, in all probability during the reign of Shar-kali-sharri. After the Akkadian empire had collapsed, Puzur-Mama became fully independent, assuming the title of "King of Lagash"" in Álvarez-Mon, Javier; Basello, Gian Pietro; Wicks, Yasmina (2018). The Elamite World. Routledge. p. 254. ISBN 978-1-317-32983-1.
- ^ The Cambridge Ancient History. Cambridge University Press. 1971. p. 998.
- ^ a b Zettler (2003), pp. 24–25. "Moreover, the Dynasty of Akkade's fall did not lead to social collapse, but the re-emergence of the normative political organization. The southern cities reasserted their independence, and if we know little about the period between the death of Sharkalisharri and the accession of Urnamma, it may be due more to accidents of discovery than because of widespread 'collapse.' The extensive French excavations at Tello produced relevant remains dating right through the period."
- ^ "CDLI-Found Texts". cdli.ucla.edu.
- ^ "Cylinder Seal with King or God and Vanquished Lion". The Walters Art Museum.
- ^ Norman Yoffee, "The Collapse of Ancient Mesopotamian States and Civilization", In The Collapse of Ancient States and Civilizations, ed. Norman Yoffee and George L. Cowgill, University of Arizona Press, 1991. Cited in Zettler (2003), p. 22: "Yoffee [...] argued that unification of the formerly independent city-states of the southern floodplain created an inherently unstable polity, generating an 'uneasy' power sharing between local elites and royal appointees particularly apparent in the redistribution of provincial lands to royal officials and the requisitioning of labor and resources. [...] Yoffee cited certain external factors as contributing to the collapse of the Dynasty of Akkade as well. he suggested that the Dynasty was 'overextended,' and resurrected Speiser's argument that the projection of Akkadian military power in distant regions 'galvanized' local populations such as the Guti, inducing them to form alliances and conduct 'guerrilla' operations against the Akkadians."
- ^ Richard A. Kerr (1998). "Sea-Floor Dust Shows Drought Felled Akkadian Empire". Science. 279 (5349): 325–326. Bibcode:1998Sci...279..325K. doi:10.1126/science.279.5349.325.
- ^ "Unreported Heritage News".
- ^ deMenocal P.B., (2000), "North Atlantic influence on Tigris–Euphrates streamflow" (International Journal of Climatology, Volume 20, Issue 8, pages 853–863, 30 June 2000)
- ^ Cookson, Evangeline; Hill, Daniel J.; Lawrence, Dan (1 June 2019). "Impacts of long term climate change during the collapse of the Akkadian Empire". Journal of Archaeological Science. 106: 1–9. doi:10.1016/j.jas.2019.03.009. ISSN 0305-4403. Archived from the original on 2 May 2019.
- ^ "Cylinder Seal of Ibni-Sharrum". Louvre Museum.
- ^ "Site officiel du musée du Louvre". cartelfr.louvre.fr.
- ^ Brown, Brian A.; Feldman, Marian H. (2013). Critical Approaches to Ancient Near Eastern Art. Walter de Gruyter. p. 187. ISBN 9781614510352.
- ^ Christie, Peter (2008) The Curse of Akkad: Climate Upheavals that Rocked Human History, Annick Press, pp. 31–48
- ^ deMenocal, Peter B. (2001). "Cultural Responses to Climate Change During the Late Holocene" (PDF). Science. 292 (5517): 667–673. doi:10.1126/science.1059287.
- ^ "Climate change and the collapse of the Akkadian empire: Evidence from the deep sea" Geology 28(4), April 2000.
- ^ Zettler (2003), pp. 18–21.
- ^ J. Oates (2004), p. 11–13. "A French soil-micomorphologist, Marie-Agnés County, a leading figure in assessing the evidence for this 'event', has now identified at Brak the earliest clearly dated Near Eastern soil 'signal' in a level unquestionably preceding the construction of Naram-Sin's Palace, that is, well before the collapse of the Akkadian Empire (see Courty 2001 and associated bibliography)."
- ^ Watanabe, Takaaki K.; Watanabe, Tsuyoshi; Yamazaki, Atsuko; Pfeiffer, Miriam (2019). "Oman corals suggest that a stronger winter shamal season caused the Akkadian Empire (Mesopotamia) collapse". Geology. GeoScienceWorld. 47 (12): 1141–1145. doi:10.1130/G46604.1.
- ^ "Strong winter dust storms may have caused the collapse of the Akkadian Empire". Hokkaido University. 24 October 2019.
- ^ Leick, Gwendolyn (2001) "Mesopotamia: Invention of the City" (Penguin Books)
- ^ [2] Tar'am-Agade, Daughter of Naram-Sin, at Urkesh, Buccellati, Giorgio and Marilyn Kelly-Buccellati, in of Pots and Plans. Papers on the Archaeology and History of Mesopotamia and Syria presented to David Oates in Honour of his 75th Birthday, London: Nabu Publications, 2002
- ^ J. Oates (2004), p. 10.
- ^ "Cylinder seal of Ubil-Eshtar". British Museum.
- ^ Thompson, William J. (2003), "Complexity, Diminishing Marginal Returns and Serial Mesopotamian Fragmentation," Journal of World Systems Research
- ^ Leick Gwendolyn (2003), "Mesopotamia: The invention of the city" (Penguin)
- ^ Kramer 1963:324, quoted in Charles Keith Maisels, The Emergence of Civilization ch. "The institutions of urbanism", 1990:179.
- ^ Bourke, Stephen (2008). The Middle East: the cradle of civilization revealed. Thames & Hudson. p. 89. ISBN 9780500251478.
- ^ Ray, Himanshu Prabha (2003). The Archaeology of Seafaring in Ancient South Asia. Cambridge University Press. p. 85. ISBN 9780521011099.
- ^ "The Indus Civilization and Dilmun, the Sumerian Paradise Land". www.penn.museum.
- ^ a b Reade, Julian E. (2008). The Indus-Mesopotamia relationship reconsidered (Gs Elisabeth During Caspers). Archaeopress. pp. 14–17. ISBN 978-1-4073-0312-3.
- ^ Stein, Stephen K. (2017). The Sea in World History: Exploration, Travel, and Trade [2 volumes]. ABC-CLIO. p. 38. ISBN 9781440835513.
- ^ McKeon, John F. X. (1970). "An Akkadian Victory Stele". Boston Museum Bulletin. 68 (354): 239. ISSN 0006-7997. JSTOR 4171539.
- ^ Frankfort, Henri, The Art and Architecture of the Ancient Orient, Pelican History of Art, 4th ed 1970, Penguin (now Yale History of Art), ISBN 0140561072, pp. 83–91
- ^ Frankfort, p. 91
- ^ Art of the First Cities: The Third Millennium B.C. from the Mediterranean to the Indus. Metropolitan Museum of Art. 2003. pp. 204–205. ISBN 978-1-58839-043-1.
- ^ McKeon, John F. X. (1970). An Akkadian Victory Stele. pp. 226–243.
- ^ "The Adda Seal". British Museum.
- ^ "Sumerian language". Encyclopædia Britannica.
- ^ Winter, Irene J. (1987), "Women in Public: The Disk of Enheduanna, The Beginning of the Office of En-Priestess, the Weight of the Visual Evidence." La Femme dans le Proche-Orient Antique. (Paris: Editions Recherche sur les Civilisations)
- ^ Enheduanna, The Exaltation of Inanna. Translated by William W. Hallo and J.J.A. Van Dijk, Ams Pr Inc, 1979, ISBN 0-404-60263-0
- ^ Binkley, Roberta, The Importance of Enheduanna
- ^ "The Electronic Text Corpus of Sumerian Literature".
- ^ Jerrold S. Cooper, "Paradigm and Propaganda: The Dynasty of Akkade in the 21st Century"; in Liverani (1993).
- ^ Bill T. Arnold, "The Weidner Chronicle and the Idea of History in Israel and Mesopotamia; in Faith, Tradition, and History: Old Testament Historiography in Its Near Eastern Context; Millard, Hoffmeier & Baker, eds.; Winona Lake, Indiana: Eisenbrauns, 1994; ISBN 0-931464-82-X; p. 138.
- ^ van de Mieroop, M. (2007). A History of the Ancient Near East, ca. 3000–323 BC. Malden: Blackwell. pp. 68–69. ISBN 978-0-631-22552-2.
Bibliography[edit]
- Liverani, Mario, ed. (1993). Akkad: The First World Empire: Structure, Ideology Traditions". Padova: Sargon srl. ISBN 978-8-81120-468-8
- Oates, Joan (2004). "Archaeology in Mesopotamia: Digging Deeper at Tell Brak". 2004 Albert Reckitt Archaeological Lecture. In Proceedings of the British Academy: 2004 Lectures; Oxford University Press, 2005. ISBN 978-0-19726-351-8.
- Sallaberger, Walther; Westenholz, Aage (1999), Mesopotamien. Akkade-Zeit und Ur III-Zeit, Orbis Biblicus et Orientalis, 160/3, Göttingen: Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht, ISBN 978-3-525-53325-3
- E. A. Speiser, Some Factors in the Collapse of Akkad, Journal of the American Oriental Society, vol. 72, no. 3, pp. 97–101, (Jul. - Sep. 1952)
- Zettler, Richard L. (2003). "Reconstructing the World of Ancient Mesopotamia: Divided Beginnings and Holistic History". Journal of the Economic and Social History of the Orient. 46 (1): 3–45. doi:10.1163/156852003763504320. JSTOR 3632803.
External links[edit]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Akkadian Empire. |
- Iraq's Ancient Past – Penn Museum
- Year Names of Narim-Sin – CDLI
- Year Named of Shar-kali-Sharri – CDLI
- Site on Enheduanna at Virginia Tech University
- States and territories established in the 3rd millennium BC
- States and territories disestablished in the 3rd millennium BC
- Akkadian Empire
- Assyrian geography
- Ancient Mesopotamia
- Ancient Upper Mesopotamia
- Levant
- 24th-century BC establishments
- 3rd-millennium BC disestablishments
- Former monarchies of Asia
- Nimrod













